109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

动脉内化疗栓塞与放疗结合与否对肝细胞肝癌合并门静脉癌栓的疗效比较: 一项综合分析
Authors Zhao Q, Zhu K, Yue J, Qi Z, Jiang S, Xu X, Feng R, Wang R
Received 31 October 2016
Accepted for publication 30 November 2016
Published 22 December 2016 Volume 2017:13 Pages 21—31
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S126181
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Purpose: Numerous studies have tried to combine transarterial chemoembolization
(TACE) or hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) with radiotherapy (RT)
for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with portal vein
tumor thrombus (PVTT). However, the efficacy of TACE or HAIC combined with RT
versus TACE or HAIC alone remains controversial. Thus, we performed a
meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of intra-arterial
chemoembolization combined with RT versus intra-arterial chemoembolization
alone for the treatment of HCC patients with PVTT.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were systematically
searched for eligible studies. Two authors independently reviewed the
abstracts, extracted relevant data and rated the quality of studies. The major
end points were objective response rate (ORR), overall survival (OS), and
adverse events.
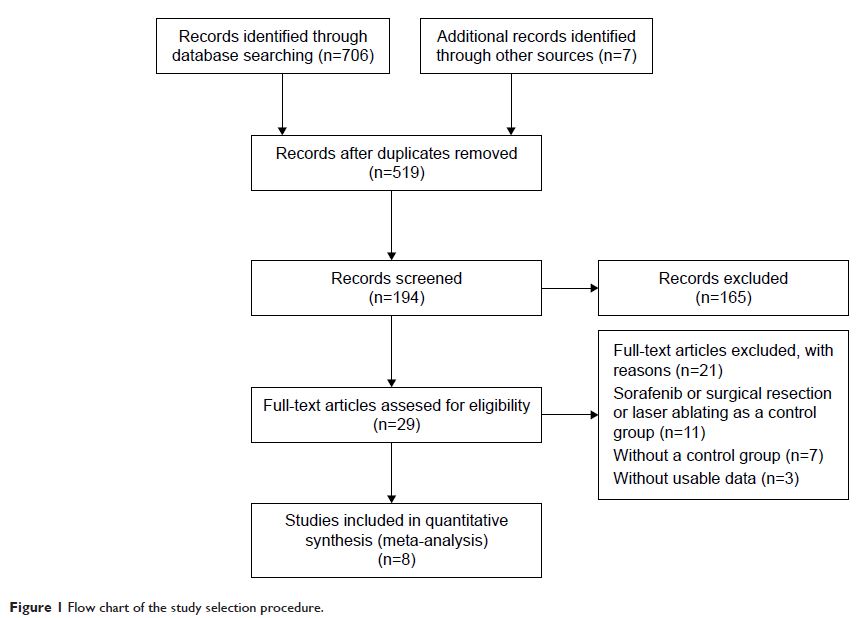
Results: Eight studies with a total of 1,760 patients were included in this
meta-analysis. The pooled results showed that intra-arterial chemoembolization
combined with RT significantly improved ORR of PVTT (OR, 4.22; 95% CI,
3.07–5.80; P <0.001) and OS (HR, 0.69; 95%
CI, 0.57–0.83; P =0.001), but did
not affect ORR of primary liver tumor (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 0.67–2.79; P =0.390).
The incidence of grade 3 or 4 leukopenia (OR, 5.80; 95% CI, 2.478–13.56; P <0.001) and thrombocytopenia
(OR, 3.77; 95% CI, 1.06–13.43; P =0.041) was higher
in the intra-arterial chemoembolization plus RT group than in the
intra-arterial chemoembolization group.
Conclusion: Combination therapy of intra-arterial chemoembolization and RT for HCC
patients with PVTT could bring higher ORR of PVTT and better survival benefits.
This combination therapy was also associated with a significantly increased
risk of adverse events. However, they were mostly mild to moderate and
successfully treated with conservative treatment.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, portal vein tumor thrombus, intra-arterial chemoembolization,
radiotherapy, meta-analysis