109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由固体脂质纳米颗粒递送的姜黄素 (Curcumin) 之增强的光细胞毒性
Authors Jiang S, Zhu R, He X, Wang J, Wang M, Qian Y, Wang S
Received 24 September 2016
Accepted for publication 10 November 2016
Published 22 December 2016 Volume 2017:12 Pages 167—178
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S123107
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jia Fan
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Curcumin (Cur) is a promising photosensitizer that could be used in
photodynamic therapy. However, its poor solubility and hydrolytic instability
limit its clinical use. The aim of the present study was to encapsulate Cur
into solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) in order to improve its therapeutic
activity. The Cur-loaded SLNs (Cur-SLNs) were prepared using an emulsification
and low-temperature solidification method. The functions of Cur and Cur-SLNs
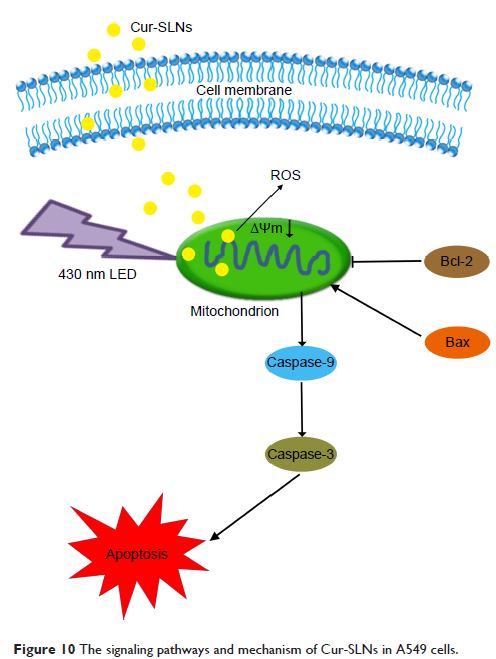
were studied on the non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells for photodynamic therapy.
The results revealed that Cur-SLNs induced ~2.27-fold toxicity higher than free
Cur at a low concentration of 15 µM under light excitation, stocking more cell
cycle at G2/M phase. Cur-SLNs could act as an efficient drug delivery system to
increase the intracellular concentration of Cur and its accumulation in
mitochondria; meanwhile, the hydrolytic stability of free Cur could be
improved. Furthermore, Cur-SLNs exposed to 430 nm light could produce more
reactive oxygen species to induce the disruption of mitochondrial membrane
potential. Western blot analysis revealed that Cur-SLNs increased the
expression of caspase-3, caspase-9 proteins and promoted the ratio of
Bax/Bcl-2. Overall, the results from these studies demonstrated that the SLNs
could enhance the phototoxic effects of Cur.
Keywords: photodynamic
therapy, curcumin, solid lipid nanoparticles, drug delivery, reactive oxygen
species