109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

AZGP1 的减少可预测中国北方食管鳞状细胞癌患者的预后不良
Authors Tang H, Wu Y, Qin Y, Wang H, Wang L, Guan X, Luo S, Wang Q
Received 31 May 2016
Accepted for publication 8 November 2016
Published 20 December 2016 Volume 2017:10 Pages 85—94
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S113932
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: As a key regulator in lipid mobilization, AZGP1 has been reported to
play a significant role in various cancers. This study was carried out to
investigate the role of AZGP1 in the development of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (ESCC) patients in Northern China.
Materials and methods: Through the application of quantitative real-time
polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining, AZGP1 expression in
ESCC tissues from Northern China was examined.
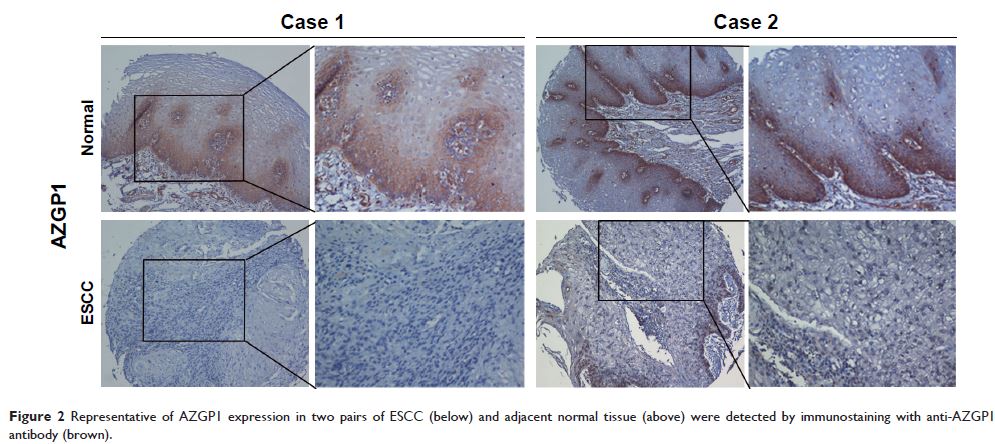
Results: Decreased expression of AZGP1 was observed in ~60%
ESCC patients. AZGP1 downregulation was significantly associated with lymph
node metastasis (P =0.035), advanced
clinical stage (P =0.018), poor prognosis for
5-year disease-specific survival (DSS; P <0.001), local recurrence-free
survival (LRFS; P =0.016), and metastasis-free
survival (MeFS; P =0.014). In addition, Cox
multivariate analysis revealed that AZGP1 downregulation remained to be an
independent prognosticator for shorter DSS (P =0.001), LRFS (P =0.011), and MeFS (P =0.004).
Conclusion: AZGP1 might be a candidate tumor suppressor and a
potential novel prognostic biomarker for ESCC patients in Northern China.
Keywords: AZGP1, ESCC, prognosis, Northern China