109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

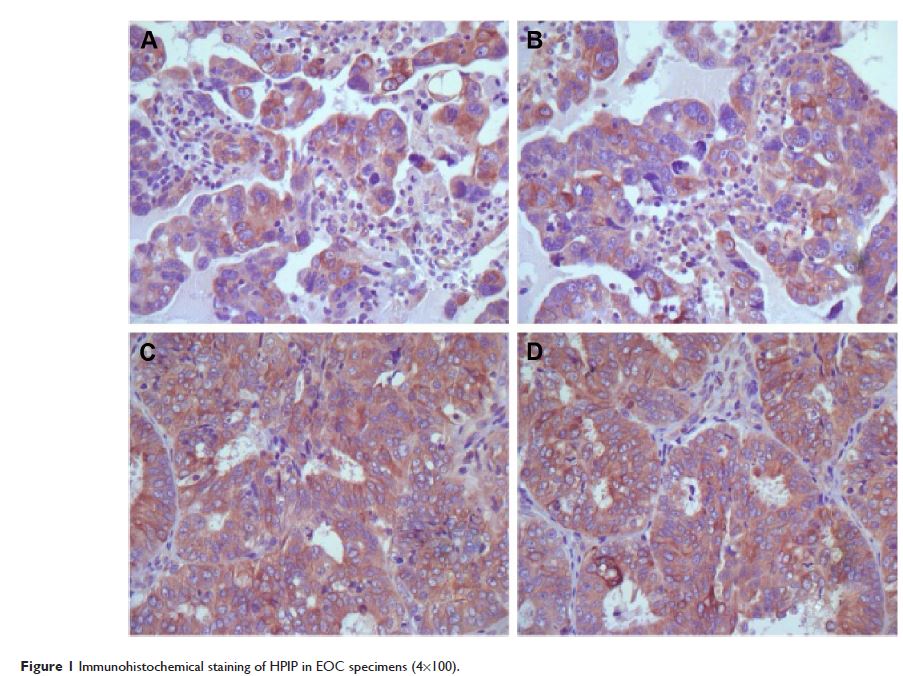
在上皮性卵巢癌中的 HPIP 表达:一项临床病理学研究
Authors Wang Y, Meng F, Liu Y, Chen X
Received 13 June 2016
Accepted for publication 10 August 2016
Published 20 December 2016 Volume 2017:10 Pages 95—100
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S114884
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Objectives: Hematopoietic pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor (PBX)-interacting
protein (HPIP) plays an important role in cancer invasion and metastasis. The
aim of this study is to investigate the expression of HPIP in epithelial
ovarian cancer (EOC).
Patients and methods: Immunohistochemical method was performed using 42
normal ovarian specimens and 145 specimens with EOC. The correlations of HPIP
expression with the clinicopathological factors and prognosis of EOC patients
were evaluated. Statistical analyses were performed using the chi-square test,
multivariate Cox proportional hazard, and Kaplan–Meier method.
Results: HPIP expression in EOC was higher than that in normal
tissues (P <0.001). HPIP expression was
significantly associated with histological grade, International Federation of
Gynecology and Obstetrics stage, and lymphatic metastasis of EOC (P <0.05). Patients with high
HPIP expression had poorer overall survival and disease-free survival (P <0.001) compared with patients
with low HPIP expression. Multivariate Cox analysis demonstrated that HPIP was
an independent factor for overall survival and disease-free survival (P <0.05).
Conclusion: HPIP may be a valuable biomarker for predicting the
prognosis of EOC patients and may serve as a potential target for cancer
therapy.
Keywords: hematopoietic
pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor-interacting protein, epithelial
ovarian cancer, immunohistochemistry, prognosis