109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低水平 PLCE1 与肝细胞癌的预后不良相关
Authors Cheng Y, Xing SG, Jia WD, Huang M, Bian NN
Received 2 November 2016
Accepted for publication 23 November 2016
Published 19 December 2016 Volume 2017:10 Pages 47—54
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S126401
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ru Chen
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Previous reports show that phospholipase C epsilon-1 (PLCE1 ) expression is positively
correlated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cardia
adenocarcinomas; however, the expression of PLCE1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and
its correlation with clinical outcome still remain unclear. The aim of this
study was to explore the expression of PLCE1 in HCC tissue and to determine whether PLCE1 was a prognostic factor for HCC patients.
Materials and
methods: PLCE1 levels in 20 paired HCC tissues and corresponding paracarcinomatous
tissues was investigated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
and Western blot assays. In addition, protein levels of PLCE1 in one normal liver epithelial cell
and four HCC cell lines were examined using Western blot assay. Moreover,
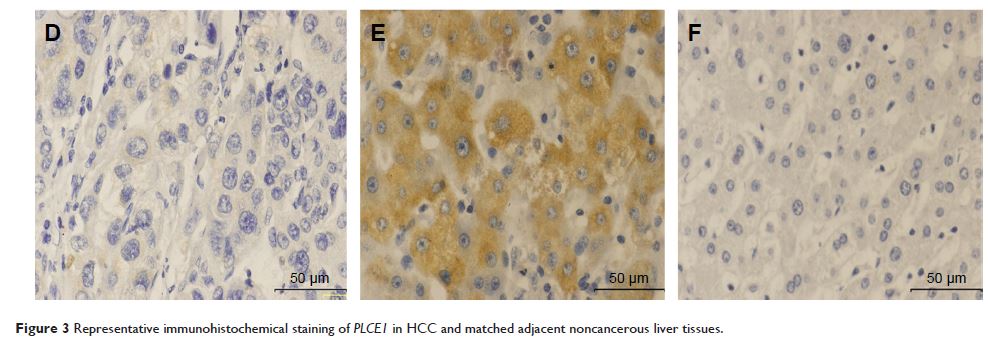
immunohistochemistry was applied to determine the expression of PLCE1 in HCC and corresponding surrounding
tissues from 90 patients. Statistical analyses were used to examine the
association between PLCE1 levels and clinicopathological
features.
Results: We found that the expression of PLCE1 in tumor tissues was significantly
lower than those in paracarcinomatous tissues at both mRNA and protein levels (P <0.05). We also determined
that PLCE1 protein expression levels were lower
in HCC cell lines than normal liver epithelial cells (P <0.05). Notably,
immunohistochemical assay showed that PLCE1 expression was significantly low in
HCC tissues compared with the adjacent normal liver tissues (40% vs 18.9%; P <0.05).
Besides, PLCE1 levels were negatively correlated with
tumor capsulae, vascular invasion, Edmondson grade, alpha-fetoprotein, and
tumor-node-metastasis stage (P <0.05).
Univariate analysis revealed that lower level expression of PLCE1 was significantly associated with
poorer overall survival (OS) rate (P <0.001) and
disease-free survival rate (P <0.001).
Multivariate analysis revealed that low PLCE1 level was an
independent poor prognostic factor of OS and recurrence-free survival (P <0.001 and P =0.003,
respectively).
Conclusion: In brief, our results revealed that decreased PLCE1 expression was associated with tumor
progression in HCC and may function as a promising biomarker for HCC prognosis.
Keywords: PLCE1 , hepatocellular carcinoma, prognosis, immunohistochemistry