109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

将地黄多糖 (Rehmannia glutinosa ) 脂质体作为一个新的治疗策略以刺激有效的免疫应答及其对树突细胞的作用
Authors Huang Y, Qin T, Huang Y, Liu Z, Bo R, Hu Y, Liu J, Wu Y, Wang D
Received 5 August 2016
Accepted for publication 10 November 2016
Published 14 December 2016 Volume 2016:11 Pages 6795—6808
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S119108
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Nanomedicine, the medical application of nanotechnology, promises a
seemingly limitless range of applications from drug delivery to adjuvants and
therapeutics. Our current research is focused on natural polymer-based liposome
adjuvants. With the aim of inducing protective and long-lasting immunity, the
immunological adjuvant activity of Rehmannia glutinosa polysaccharide liposome (RGPL) was
investigated. In vivo, the splenic lymphocyte proliferation ratios and
ovalbumin-specific immunoglobulin G titers of ovalbumin-RGPL-vaccinated mice
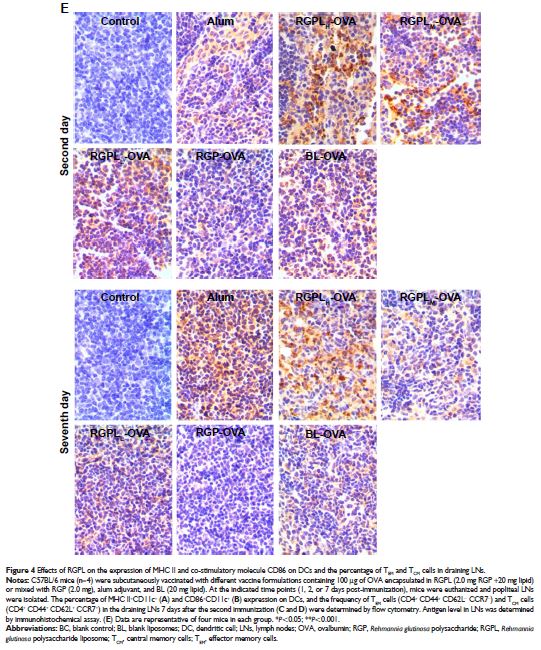
were significantly upregulated. In draining lymph nodes, the expression of MHC
II+CD11c+ and CD86+CD11c+ was
increased by RGPL; in addition, the percentages of central memory cells (TCM) and effector memory cells (TEM) were also elevated. RGPL could effectively provide
adequate antigen exposure in lymph nodes. In vitro, RGPL could promote
dendritic cell maturation and enhance dendritic cell functions, such as the
mixed lymphocyte reaction and antigen presentation. Overall, the results
demonstrated that RGPL has the potential to act as an effective controlled
release vaccine adjuvant.
Keywords: Rehmannia glutinosa polysaccharide liposome, adjuvant,
controlled release, ovalbumin, dendritic cells