109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

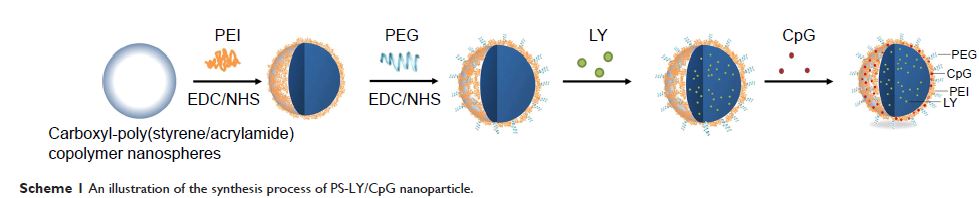
聚乙烯亚胺改性的羧基 - 聚苯乙烯/丙烯酰胺共聚物纳米球用于共同递送对小鼠中肝癌有显著肿瘤消退作用的 CpG 和 TGF-β 受体I抑制剂
Authors Liang SY, Hu J, Xie YY, Zhou Q, Zhu YH, Yang XL
Received 10 September 2016
Accepted for publication 4 November 2016
Published 13 December 2016 Volume 2016:11 Pages 6753—6762
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122047
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Yashdeep Phanse
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Cancer immunotherapy based on nanodelivery systems has shown potential
for treatment of various malignancies, owing to the benefits of tumor targeting
of nanoparticles. However, induction of a potent T-cell immune response against
tumors still remains a challenge. In this study, polyethylenimine-modified
carboxyl-styrene/acrylamide (PS) copolymer nanospheres were developed as a
delivery system of unmethylated cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG)
oligodeoxynucleotides and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) receptor I
inhibitors for cancer immunotherapy. TGF-β receptor I inhibitors (LY2157299,
LY) were encapsulated to the PS via hydrophobic interaction, while CpG
oligodeoxynucleotides were loaded onto the PS through electrostatic
interaction. Compared to the control group, tumor inhibition in the PS-LY/CpG
group was up to 99.7% without noticeable toxicity. The tumor regression may be
attributed to T-cell activation and amplification in mouse models. The results
highlight the additive effect of CpG and TGF-β receptor I inhibitors
co-delivered in cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: CpG, TGF-β receptor I inhibitor,
Pst-AAm copolymer nanosphere, immunotherapy