109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过弥散加权成像和表观弥散系数评价放化疗在子宫颈癌治疗中的疗效
Authors Ju F
Received 2 May 2016
Accepted for publication 28 September 2016
Published 13 December 2016 Volume 2016:9 Pages 7555—7561
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S111829
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in
cervical cancer using diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with apparent diffusion
coefficient (ADC) values.
Methods: A total of 71 patients with cervical cancer were
enrolled in this study. All patients underwent conventional magnetic resonance
imaging and DWI scanning before CRT and at 7, 14, 21 days, and 6 months after
CRT. These patients were divided into the complete response (CR) and non-CR
groups according to the response evaluation criteria in solid tumors criteria.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the accuracy
of ADC values in predicting the efficacy of CRT in cervical cancer.
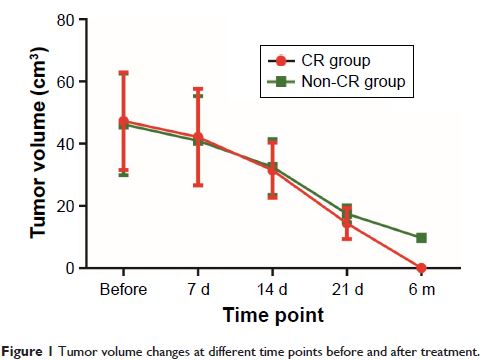
Results: Compared with before-CRT treatment,
tumor volumes were reduced and ADC values were elevated in both CR and non-CR
groups after CRT treatment. At 21 days after CRT, tumor volumes in the CR group
were smaller than those in the non-CR group. During the period of 21 days to
6 months after CRT, tumor regression rate and the increased rate of ADC values
in the CR group were higher than those in the non-CR group. ROC curves revealed
that the increased rate of ADC values at 21 days after CRT was the optimal time
point for the prediction of CRT efficacy in cervical cancer, with the area
under the curve, sensitivity, and specificity of 0.775, 92.7%, and 62.5%,
respectively.
Conclusion: Our study provides evidence that the increased rate of
ADC at 21 days after CRT might be a promising tool for predicting the efficacy
of CRT in cervical cancer.
Keywords: diffusion-weighted imaging, cervical
cancer, apparent diffusion coefficient, chemoradiotherapy, efficacy