109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

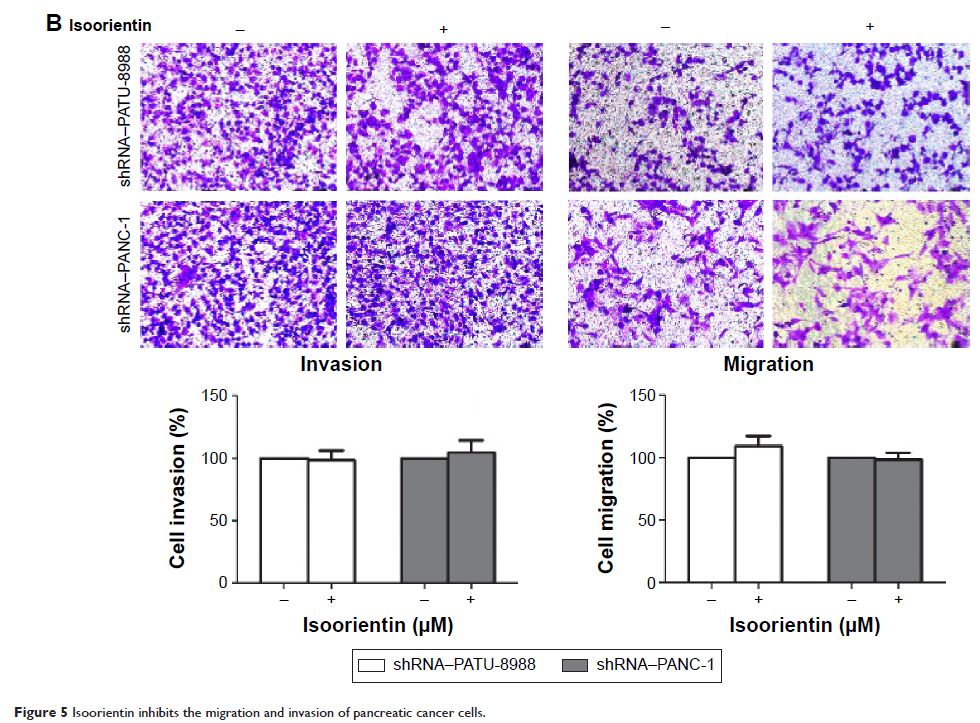
更正启 事 — 同工素 (Isoorientin or homoorientin) 可诱导细胞凋亡、降低侵袭性,并通过活化胰腺癌细胞中的 AMPK 信号使 VEGF 分泌下调
Authors Ye T, Su J, Huang C, Yu D, Dai S, Huang X, Chen B, Zhou M
Received 18 September 2016
Accepted for publication 8 November 2016
Published 12 December 2016 Volume 2016:9 Pages 7481—7492
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S122653
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Abstract: Isoorientin (or homoorientin) is a flavone, which is a chemical
flavonoid-like compound, and a 6-C-glucoside of luteolin. Isoorientin has been
demonstrated to have anti-cancer activities against various tumors, but its
effects on pancreatic cancer (PC) have not been studied in detail. In this
study, we aim to investigate whether isoorientin has potential anti-PC effects
and its underlying mechanism. In PC, isoorientin strongly inhibited the
survival of the cells, induced cell apoptosis, and decreased its malignancy by
reversing the expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and matrix
metalloproteinase and decreased vascular endothelial growth factor expression.
Meanwhile, we investigated the activity of the AMP-activated protein kinase
(AMPK) signaling pathway after isoorientin treatment, which was forcefully
activated by isoorientin, as expected. In addition, in the PC cells that were
transfected with lentivirus to interfere with the expression of the gene PRKAA1 , there were
no differences in the apoptosis rate and the expression of malignancy
biomarkers in the tumors of the isoorientin-treated and untreated groups. Thus,
we demonstrated that isoorientin has potential antitumor effects via the AMPK
signaling pathway, and isoorientin merits further investigation.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, AMPK, isoorientin,
apoptosis, invasiveness, VEGF
*本文作者告知在文章中的一些图表出现了一些错误。
请点击这里查看详细更正启事