109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂功效与晚期非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC) 患者的循环肿瘤细胞水平之间的相关性
Authors He W, Li W, Jiang B, Chang L, Jin C, Tu C, Li Y
Received 17 June 2016
Accepted for publication 2 September 2016
Published 12 December 2016 Volume 2016:9 Pages 7515—7520
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S115221
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the correlation between the
efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor
(EGFR-TKI) and circulating tumor cell (CTC) levels in patients with advanced
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in reducing CTC
counts in patients with advanced NSCLC was studied.
Patients and methods: A total of 66 patients with advanced NSCLC were
enrolled and divided into two groups (those with high CTC counts and those with
low CTC counts) based on the patients’ median CTC counts. All the patients were
treated with an EGFR-TKI, and the treatment efficacy and prognoses were
compared.
Results: The treatment efficacies were 53.3% (16/30) and 27.8%
(10/36) for the low CTC group and high CTC group, respectively, and this difference
was statistically significant (P <0.05). The
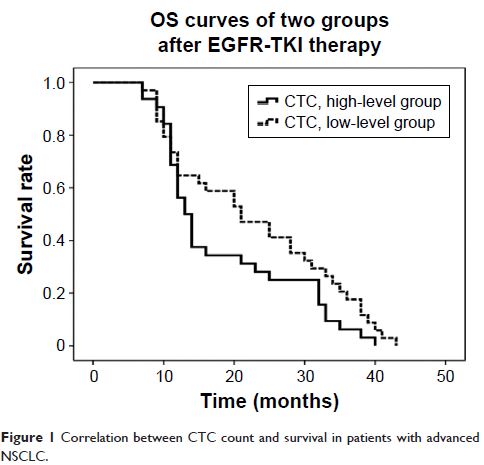
median overall survival was 22.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI]:
18.9–26.8 months) for the low CTC group and 18.3 months (95% CI:
2.9–8.2 months) for the high CTC group. The median progression-free
survival was 11.5 months (95% CI: 8.1–15 months) and 5.6 months
(95% CI: 2.9–8.2 months) for the low and high CTC groups, respectively,
and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05).
Conclusion: The CTC count can be used as an index for predicting
the EGFR-TKI effect on patients with advanced NSCLC. Efficacy and prognosis of
EGFR-TKI treatment and CTC count were considered important, and the CTC count
could be used to predict the efficacy of EGFR-TKI treatment and prognosis of
advanced NSCLC. The change in CTC expression levels can be used as an index for
evaluating the prognosis of patients with advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer,
circulating tumor cells, EGFR-TKI