109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

多巴胺 (Dopamine) 受体 D2 基因多态性与精神分裂症风险之间的关联:一项 PRISMA 兼容的综合分析
Authors He HR, Wu HH, Yang LH, Gao F, Fan YJ, Feng JQ, Ma XC
Received 1 August 2016
Accepted for publication 27 September 2016
Published 9 December 2016 Volume 2016:12 Pages 3129—3144
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S118614
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Objective: To determine the relationships between dopamine D2 receptor gene
polymorphisms and the risk of schizophrenia using meta-analysis.
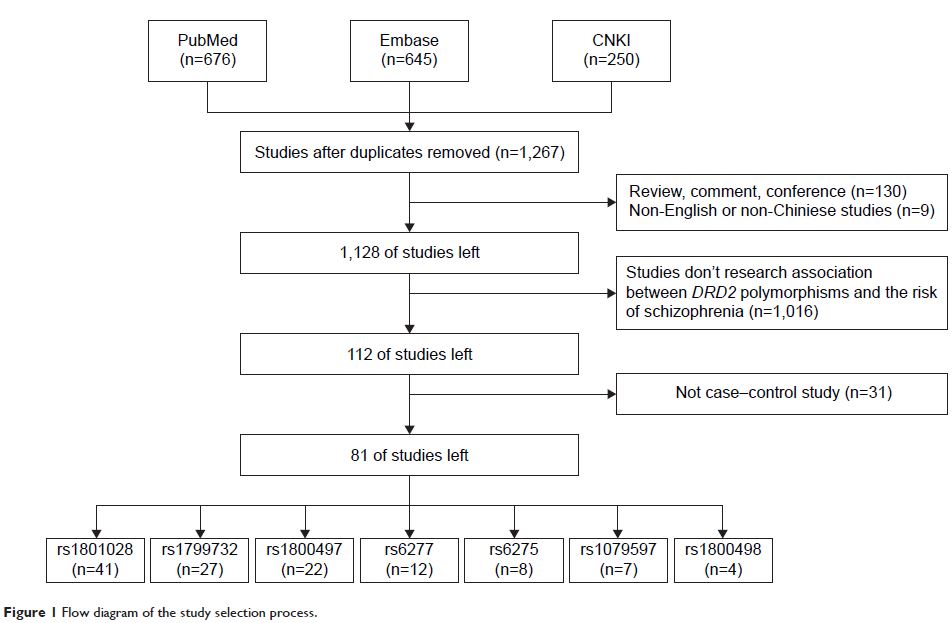
Method: The PubMed, Embase, and China National
Knowledge Infrastructure databases were searched to identify relevant
literature published up to February 2016. The allele contrast model was used.
STATA software was used for statistical analysis, with odds ratios (ORs) and
95% confidence intervals (CIs) calculated to evaluate the associations between
dopamine D2 receptor gene polymorphisms and the risk of schizophrenia.
Meta-regression and publication bias, trim-and-fill, subgroup, sensitivity,
cumulative, and fail-safe number analyses were also performed.
Results: This meta-analysis included 81 studies. The rs1801028
and rs1799732 were associated with schizophrenia risk among Asians (P =0.04, OR =1.25, 95% CI
=1.01–1.55; P <0.01, OR =0.76, 95% CI
=0.63–0.92, respectively), while the rs6277 was associated with schizophrenia
risk in Caucasians (P <0.01, OR=0.72,
95% CI =0.66–0.79). The rs1800497 was also associated with schizophrenia risk
in population-based controls (P <0.01, OR
=0.84, 95% CI =0.72–0.97). The rs6275, rs1079597, and rs1800498 were not
associated with schizophrenia risk. In addition, meta-regression indicated that
the controls may be sources of heterogeneity for the rs1801028
single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), while ethnicity may be sources of
heterogeneity for the rs6277 SNP. Publication bias was significant for the
rs1801028 SNP, and this result changed after the publication bias was adjusted
using the trim-and-fill method.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis demonstrated that the rs1801028 may
be a risk factor for susceptibility to schizophrenia among Asians, while the
rs1799732 may be a protective factor for that population. Large-sample studies
are necessary to verify the results of this meta-analysis.
Keywords: dopamine D2 receptor, polymorphisms,
schizophrenia