109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

依靠聚乙烯亚胺 (Polyethylenimine) 官能化的银纳米粒子进行的紫杉醇 (Paclitaxel) 共同传递可诱导 HepG2 细胞凋亡
Authors Li Y, Guo M, Lin Z, Zhao M, Xiao M, Wang C, Xu T, Chen T, Zhu B
Received 18 September 2016
Accepted for publication 16 November 2016
Published 8 December 2016 Volume 2016:11 Pages 6693—6702
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122666
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Hepatocarcinoma is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths
around the world. Recently, a novel emerging nanosystem as anticancer therapeutic
agents with intrinsic therapeutic properties has been widely used in various
medical applications. In this study, surface decoration of functionalized
silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by polyethylenimine (PEI) and paclitaxel (PTX) was
synthesized. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Ag@PEI@PTX
on cytotoxic and anticancer mechanism on HepG2 cells. The transmission electron
microscope image and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium
bromide assay showed that Ag@PEI@PTX had satisfactory size distribution and
high stability and selectivity between cancer and normal cells.
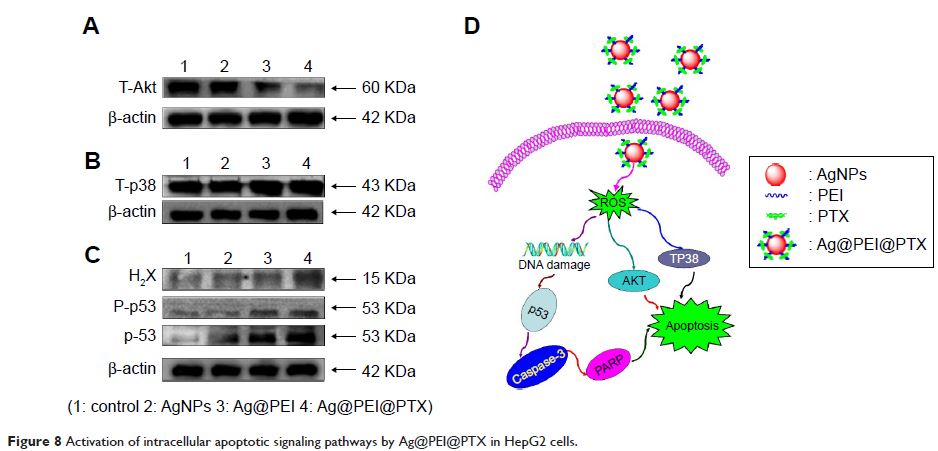
Ag@PEI@PTX-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis was confirmed by accumulation of the
sub-G1 cells population, translocation of phosphatidylserine, depletion of
mitochondrial membrane potential, DNA fragmentation, caspase-3 activation, and
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage. Furthermore, Ag@PEI@PTX enhanced
cytotoxic effects on HepG2 cells and triggered intracellular reactive oxygen
species; the signaling pathways of AKT, p53, and MAPK were activated to advance
cell apoptosis. In conclusion, the results reveal that Ag@PEI@PTX may provide
useful information on Ag@PEI@PTX-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis and as
appropriate candidate for chemotherapy of cancer.
Keywords: silver nanoparticles,
polyethylenimine, paclitaxel, reactive oxygen species, apoptosis