108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
Abl2 的过度表达预示肝细胞癌预后不良,并与肿瘤细胞迁移和侵袭相关
Authors Xing QT, Qu CM, Wang G
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 881—885
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S62348
Received 13 February 2014, Accepted 6 April 2014, Published 30 May 2014
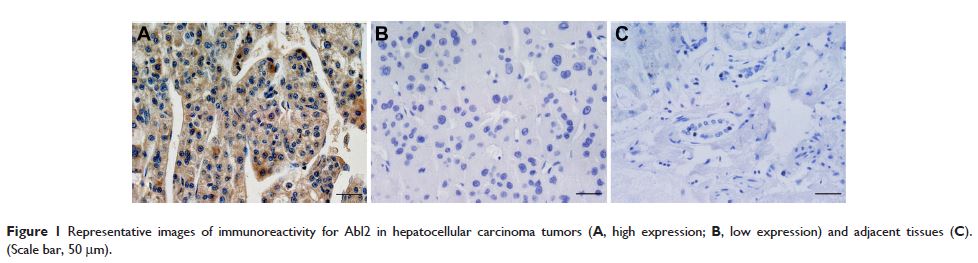
Introduction: Abl2 nonreceptor tyrosine kinase (Arg, c-abl oncogene 2) has recently been identified as being recurrently amplified at DNA levels and overexpressed at mRNA levels in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs), and might be a potential oncogenic driver and therapeutic target for HCC.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the Abl2 expression in a series of HCC tumors by immunohistochemistry and further evaluated its clinicopathological and prognostic significance. We also performed an in vitro experiment to validate the effect of Abl2 gene silencing on the migration and invasion abilities of human liver cancer HepG2 cells.
Results: It has been demonstrated that Abl2 was unregulated in 37.3% (28/75) of primary HCC tissues, and was significantly associated with a shorter overall survival time (P =0.0005). In addition, Abl2 gene silencing in HepG2 cells significantly attenuated its migration and invasion abilities in vitro. We also found that the phosphorylation of metastasis-associated gene cortactin was markedly decreased by Abl2 silencing.
Conclusion: We propose that Abl2 might be a potential candidate therapeutic target for HCCs and that targeted therapies against Abl2 in the treatment of HCCs deserve further investigation in the future.
Keywords: Abl2, Arg, HCC, metastasis, prognosis
Methods: In this study, we investigated the Abl2 expression in a series of HCC tumors by immunohistochemistry and further evaluated its clinicopathological and prognostic significance. We also performed an in vitro experiment to validate the effect of Abl2 gene silencing on the migration and invasion abilities of human liver cancer HepG2 cells.
Results: It has been demonstrated that Abl2 was unregulated in 37.3% (28/75) of primary HCC tissues, and was significantly associated with a shorter overall survival time (P =0.0005). In addition, Abl2 gene silencing in HepG2 cells significantly attenuated its migration and invasion abilities in vitro. We also found that the phosphorylation of metastasis-associated gene cortactin was markedly decreased by Abl2 silencing.
Conclusion: We propose that Abl2 might be a potential candidate therapeutic target for HCCs and that targeted therapies against Abl2 in the treatment of HCCs deserve further investigation in the future.
Keywords: Abl2, Arg, HCC, metastasis, prognosis