108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
吉非替尼在局部晚期或转移性非小细胞肺癌管理中作用的重要评价
Authors Yuan Y, Li XF, Chen JQ, Dong CX, Weng SS, Huang JJ
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 841—852
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S34124
Received 24 February 2014, Accepted 6 April 2014, Published 28 May 2014
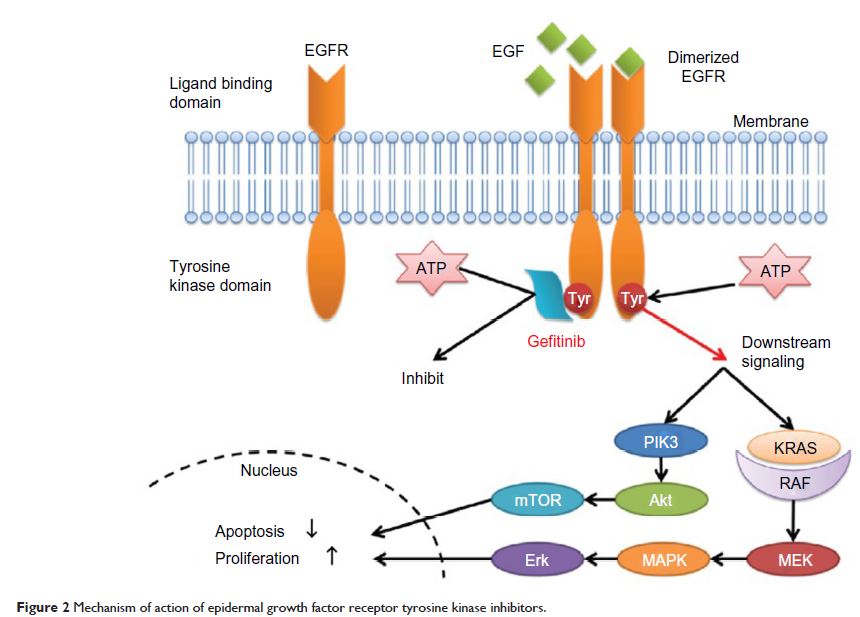
Abstract: Past studies have demonstrated that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors can significantly improve clinical outcomes in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and sensitive EGFR gene mutations. Gefitinib (Iressa®), the first oral EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has been shown to be more effective and better tolerated than chemotherapy either in first-line or second-line treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring sensitive EGFR mutations. Conversely, among patients with wild-type EGFR, gefitinib is inferior to standard chemotherapy in both the first-line and second-line settings. Further, gefitinib is effective in patients with brain metastases because of its low molecular weight and excellent penetration of the blood–brain barrier. In this review, we summarize the current data from clinical trials with gefitinib and appraise its role in the management of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
Keywords: gefitinib, non-small cell lung cancer, epidermal growth factor receptor, tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Keywords: gefitinib, non-small cell lung cancer, epidermal growth factor receptor, tyrosine kinase inhibitor