109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
通过制备碳纳米粉末固态分散体增强芹菜素的生物利用度
Authors Ding SM, Zhang ZH, Song J, Cheng XD, Jiang J, Jia XB
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 2327—2333
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S60938
Received 17 January 2014, Accepted 1 March 2014, Published 13 May 2014
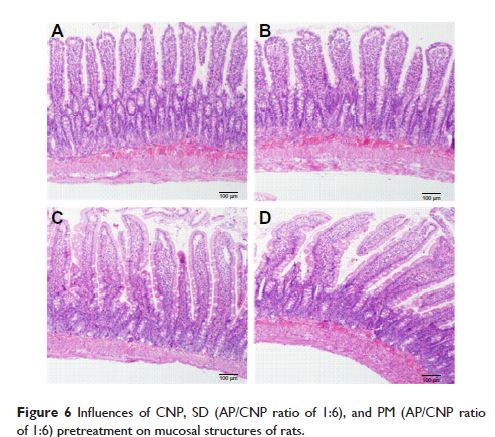
Abstract: In this study, a novel carbon nanopowder (CNP) drug carrier was developed to improve the oral bioavailability of apigenin (AP). Solid dispersions (SDs) of AP with CNP were prepared, and their in vitro drug release and in vivo performance were evaluated. The physicochemical properties of the formulations were examined by differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy. Drug release profiles showed that AP dissolution from the CNP-AP system (weight ratio, 6:1) after 60 minutes improved by 275% compared with that of pure AP. Moreover, the pharmacokinetic analysis of SD formulations in rats showed that the AP area under the curve 0–t value was 1.83 times higher for the CNP-AP system than for pure AP, indicating that its bioavailability was significantly improved. In addition, compared with pure AP, SDs had a significantly higher peak and shorter time to peak. Preliminary intestinal toxicity tests indicated that there was no significant difference in the tissues of the rats treated with the CNP-AP system, rats treated with the CNP alone, and controls. In conclusion, CNP-based SDs could be used for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs while also improving drug safety.
Keywords: apigenin, carbon nanopowder, solid dispersions, dissolution, oral bioavailability
Keywords: apigenin, carbon nanopowder, solid dispersions, dissolution, oral bioavailability