108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
手霉素诱导前列腺癌细胞的细胞凋亡
Authors Li JG, She MR, Lu CY, Wei SS, Xia PF, Lu ZS, Peng Q
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 771—777
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S60253
Received 7 January 2014, Accepted 17 March 2014, Published 22 May 2014
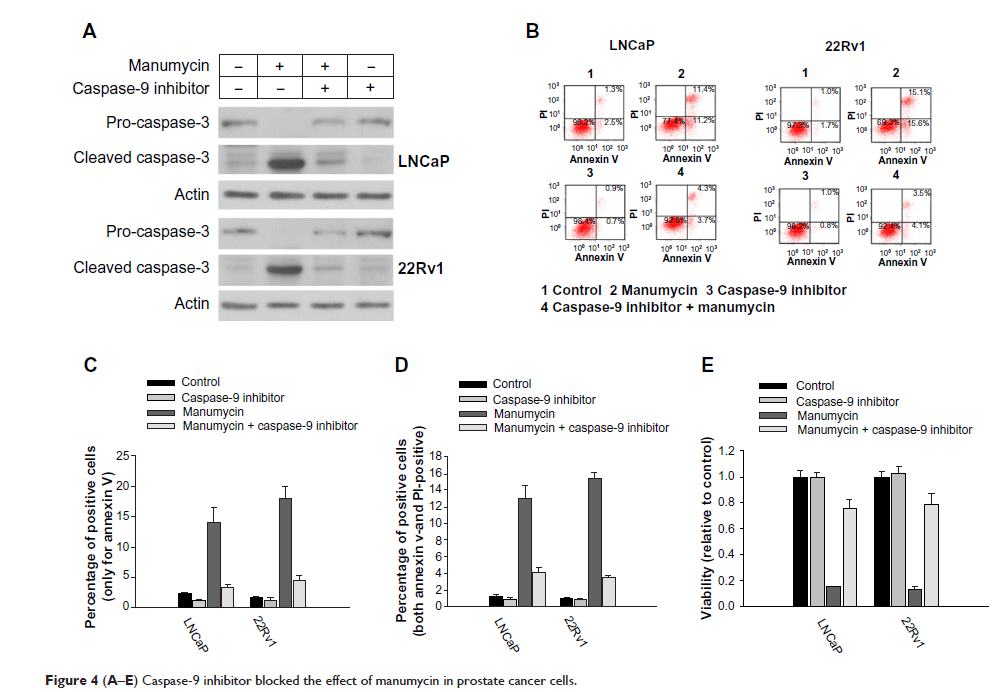
Background: Manumycin exhibits an antitumor effect in a variety of cancer cell lines, including prostate cancer cell lines (DU145 and PC-3). Our previous studies demonstrated that manumycin induced the apoptosis of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells and leukemia cells via the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. In the current study, we further evaluated the effect of manumycin in two prostate cancer cell lines (LNCaP and 22Rv1), and here we elucidate some of the underlying mechanisms.
Materials and methods: The cell viability of prostate cancer cells was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay after treatment with manumycin for 48 hours. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry using annexin V and propidium iodide. The expressions of B-cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2 family members and the activations of caspase-9 and caspase-3 were detected by Western blotting.
Results: Manumycin treatment resulted in significant decreases in the viabilities of the two prostate cancer cell lines in a dose-dependent manner through apoptosis, and this apoptosis involved caspase-9 activation. A specific inhibitor of caspase-9 protected cells from caspase-3 activation, apoptosis, and cytotoxicity induced by manumycin. We also found that manumycin downregulated Bcl-2 expression and upregulated Bax expression.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that manumycin induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through regulation of the Bcl-2 family involving caspase-9 activation. These results suggest that manumycin may be beneficial for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Materials and methods: The cell viability of prostate cancer cells was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay after treatment with manumycin for 48 hours. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry using annexin V and propidium iodide. The expressions of B-cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2 family members and the activations of caspase-9 and caspase-3 were detected by Western blotting.
Results: Manumycin treatment resulted in significant decreases in the viabilities of the two prostate cancer cell lines in a dose-dependent manner through apoptosis, and this apoptosis involved caspase-9 activation. A specific inhibitor of caspase-9 protected cells from caspase-3 activation, apoptosis, and cytotoxicity induced by manumycin. We also found that manumycin downregulated Bcl-2 expression and upregulated Bax expression.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that manumycin induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through regulation of the Bcl-2 family involving caspase-9 activation. These results suggest that manumycin may be beneficial for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Keyword: Bcl-2, farnesyltransferase inhibitor, caspase-9, caspase-3, Bax