108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
乙肝病毒感染的妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症对围产期结果的影响
Authors Hu Y, Ding YL, Yu L
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:10 Pages 381—385
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S61530
Received 29 January 2014, Accepted 25 March 2014, Published 23 May 2014
Introduction: To investigate the impact of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection on perinatal outcomes.
Methods: In the study, 200 pregnant women were divided into four groups, including 50 cases with ICP and HBV infection, 50 cases with ICP, 50 cases with HBV infection, and 50 healthy pregnancies. The delivery process and perinatal outcomes were analyzed among different groups.
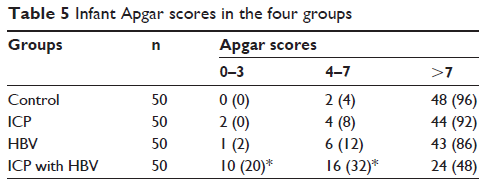
Results: When compared to the healthy pregnancy group, significantly increased rates of premature rupture of membranes, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, and cesarean section were observed in cases of ICP, HBV infection, or ICP patients with HBV (P <0.05). Specifically, the rates of HBV infection in the newborn, fetal distress, neonatal asphyxia, and birth defects in the newborn, and infant Apgar scores were higher in ICP pregnancies with HBV (56%, 48%, 16%, and 48%, respectively) than in the other groups (P <0.05).
Conclusion: ICP combined with HBV infection has a clear influence on perinatal infant outcomes.
Keywords: premature rupture of membranes, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, cesarean section, fetal distress, neonatal asphyxia, birth defects, Apgar scores
Methods: In the study, 200 pregnant women were divided into four groups, including 50 cases with ICP and HBV infection, 50 cases with ICP, 50 cases with HBV infection, and 50 healthy pregnancies. The delivery process and perinatal outcomes were analyzed among different groups.
Results: When compared to the healthy pregnancy group, significantly increased rates of premature rupture of membranes, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, and cesarean section were observed in cases of ICP, HBV infection, or ICP patients with HBV (P <0.05). Specifically, the rates of HBV infection in the newborn, fetal distress, neonatal asphyxia, and birth defects in the newborn, and infant Apgar scores were higher in ICP pregnancies with HBV (56%, 48%, 16%, and 48%, respectively) than in the other groups (P <0.05).
Conclusion: ICP combined with HBV infection has a clear influence on perinatal infant outcomes.
Keywords: premature rupture of membranes, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, cesarean section, fetal distress, neonatal asphyxia, birth defects, Apgar scores