108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
多巴胺 D1 受体基因多态性与精神分裂症的相关性:一个荟萃分析
Authors Pan YQ, Yao J, Wang BJ
Published Date June 2014 Volume 2014:10 Pages 1133—1139
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S63776
Received 8 March 2014, Accepted 15 April 2014, Published 20 June 2014
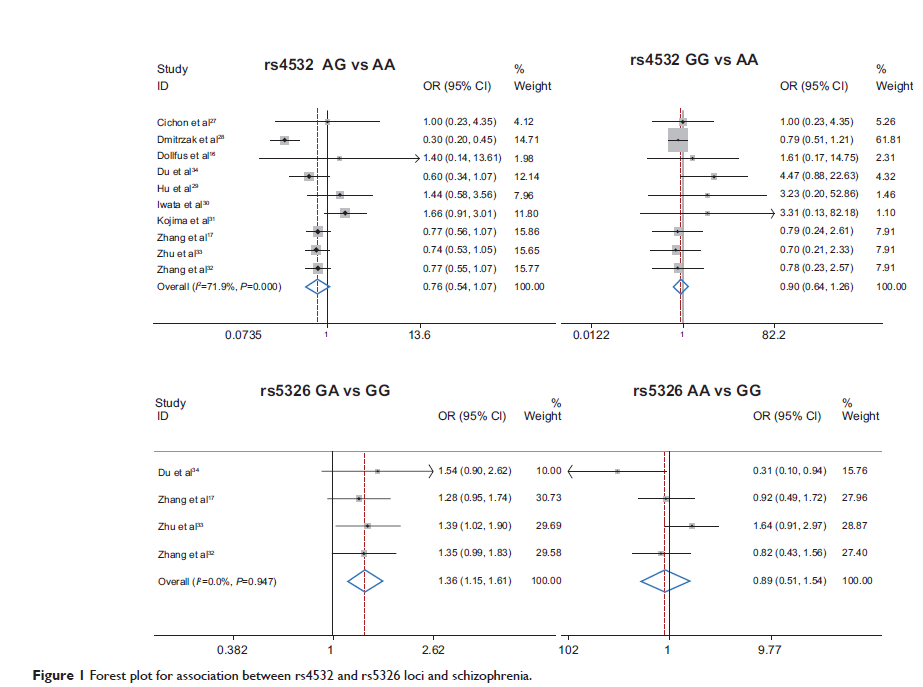
Abstract: To date, the role of dopamine D1 receptor (DRD1 ) polymorphism in schizophrenia remains controversial. We carried out a meta-analysis to determine whether DRD1 polymorphism influences the risk of schizophrenia. We examined whether rs4532 and rs5326 genetic variants are related to the etiology of schizophrenia, using a meta-analysis. Relevant case-control studies were retrieved by database searching and selected according to established inclusion criteria. A total of ten studies were identified and included in our meta-analysis, nine for rs4532, with 1,941 cases and 2,480 controls, and four for rs5326, with 1,285 cases and 1,195 controls. No significant association was found between the rs4532 locus and schizophrenia. For the rs5326 locus, the guanine-adenine (GA) genotype was associated with schizophrenia as a risk factor (for GA vs guanine-guanine [GG], odds ratio [OR] =1.36, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.15–1.61, P <0.001). The GA genotype of rs5326 increased the risk of schizophrenia, but there was no association between rs4532 and schizophrenia. These data may provide references for case-control studies in schizophrenia in future.
Keywords: susceptibility, SNP, genetics, psychiatry
Keywords: susceptibility, SNP, genetics, psychiatry