108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
米诺环素的特性及其对精神分裂症的治疗潜力
Authors Zhang L, Zhao J
Published Date June 2014 Volume 2014:10 Pages 1103—1111
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S64236
Received 17 March 2014, Accepted 22 April 2014, Published 17 June 2014
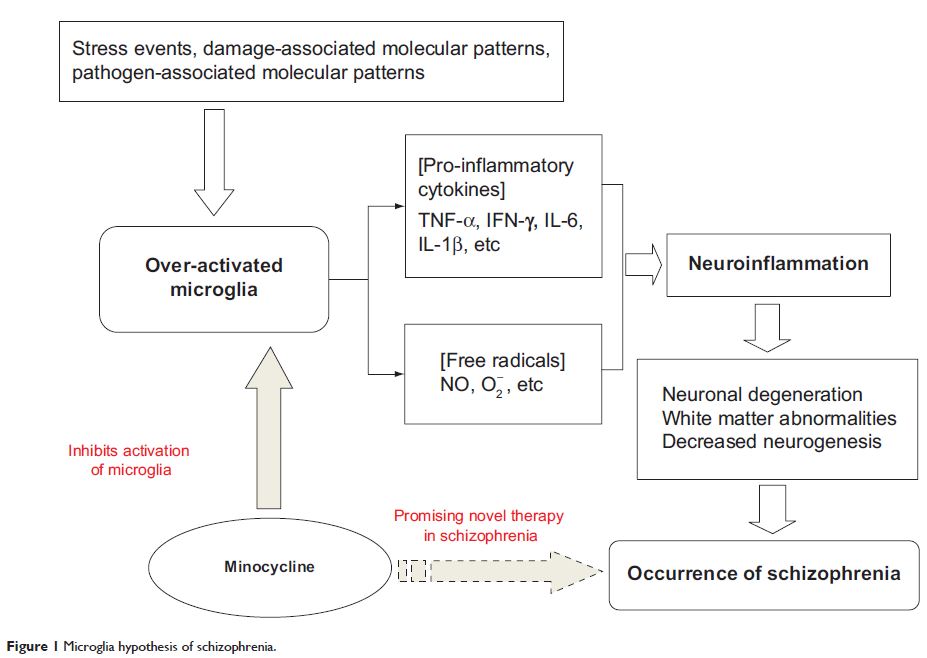
Abstract: Accumulating evidence suggests that neuroinflammation affecting microglia plays an important role in the etiology of schizophrenia, and appropriate control of microglial activation may be a promising therapeutic strategy for schizophrenia. Minocycline, a second-generation tetracycline that inhibits microglial activation, has been shown to have a neuroprotective effect in various models of neurodegenerative disease, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiapoptotic properties, and an ability to modulate glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Given that these mechanisms overlap with neuropathologic pathways, minocycline may have a potential role in the adjuvant treatment of schizophrenia, and improve its negative symptoms. Here, we review the relevant studies of minocycline, ranging from preclinical research to human clinical trials.
Keywords: schizophrenia, minocycline, microglia, neuroinflammation
Keywords: schizophrenia, minocycline, microglia, neuroinflammation