108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
通过调节 M2/M1 的巨噬细胞在肿瘤微环境中的比率,γ 干扰素和塞来昔布可抑制肺肿瘤的生长
Authors Ren F, Fan M, Mei J, Wu Y, Liu C, Pu Q, You Z, Liu L
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 1527—1538
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S66302
Received 18 April 2014, Accepted 16 July 2014, Published 23 September 2014
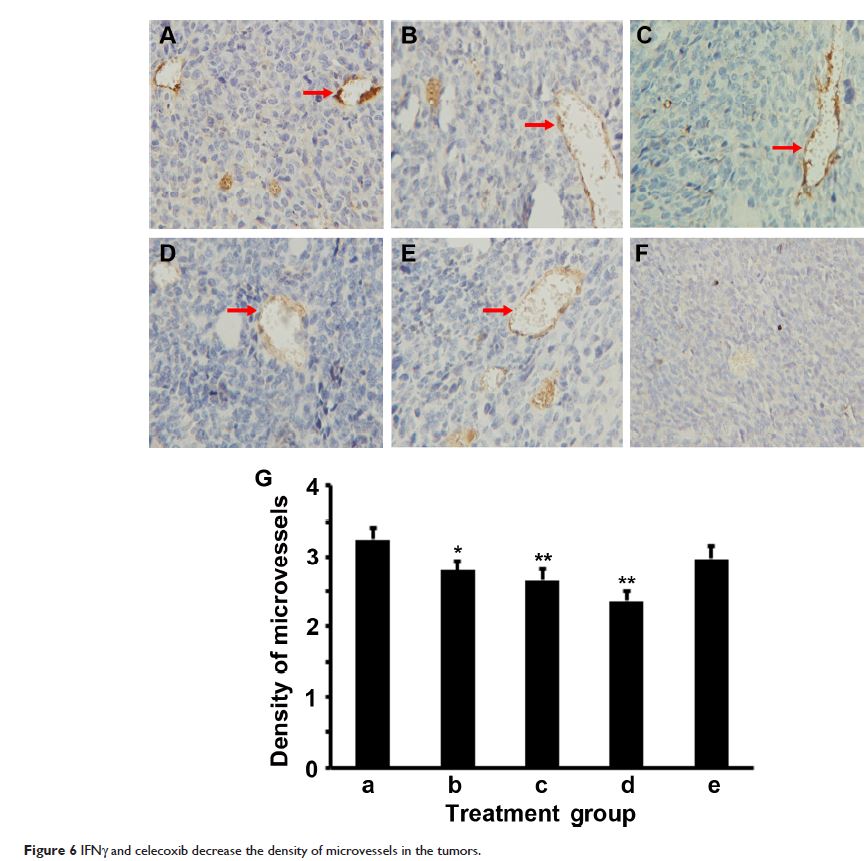
Abstract: Tumor-associated macrophages play an important role in tumor growth and progression. These macrophages are heterogeneous with diverse functions, eg, M1 macrophages inhibit tumor growth, whereas M2 macrophages promote tumor growth. In this study, we found that IFNγ and/or celecoxib (cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor) treatment consistently inhibited tumor growth in a mouse lung cancer model. IFNγ alone and celecoxib alone increased the percentage of M1 macrophages but decreased the percentage of M2 macrophages in the tumors, and thus the M2/M1 macrophage ratio was reduced to 1.1 and 1.7 by IFNγ alone and celecoxib alone, respectively, compared to the M2/M1 macrophage ratio of 4.4 in the control group. A combination of IFNγ and celecoxib treatment reduced the M2/M1 macrophage ratio to 0.8. Furthermore, IFNγ and/or celecoxib treatment decreased expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and VEGF, as well as the density of microvessels in the tumors, compared to the control group. This study provides the proof of principle that IFNγ and/or celecoxib treatment may inhibit lung-tumor growth through modulating the M2/M1 macrophage ratio in the tumor microenvironment, suggesting that IFNγ and celecoxib have potential to be further optimized into a new anticancer therapy.
Keywords: tumor-associated macrophages, M1 macrophages, M2 macrophages, lung cancer, interferon-γ, celecoxib
Keywords: tumor-associated macrophages, M1 macrophages, M2 macrophages, lung cancer, interferon-γ, celecoxib