108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
在人类口腔鳞状细胞癌中,MiR-206 充当一种肿瘤抑制子及直接靶定 K-Ras 基因
Authors Lin FO, Yao LJ, Xiao J, Liu DF, Ni ZY
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1583—1591
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S67624
Received 12 May 2014, Accepted 26 June 2014, Published 11 September 2014
Purpose: MicroRNA-206 (miR-206) has been proven to be downregulated in many human malignancies and is correlated with tumor progression. However, the roles of miR-206 and its related molecular mechanisms in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) are still unclear. Thus, the aim of this study was to explore the effects of miR-206 in OSCC tumorigenesis and development.
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to detect miR-206 expression in OSCC cell lines and primary tumor tissues. The association of miR-206 expression with clinicopathological factors and prognosis was also analyzed. In addition, the effects of miR-206 on the biological behavior of OSCC cells were investigated. Lastly, the potential regulatory function of miR-206 on K-Ras expression was confirmed.
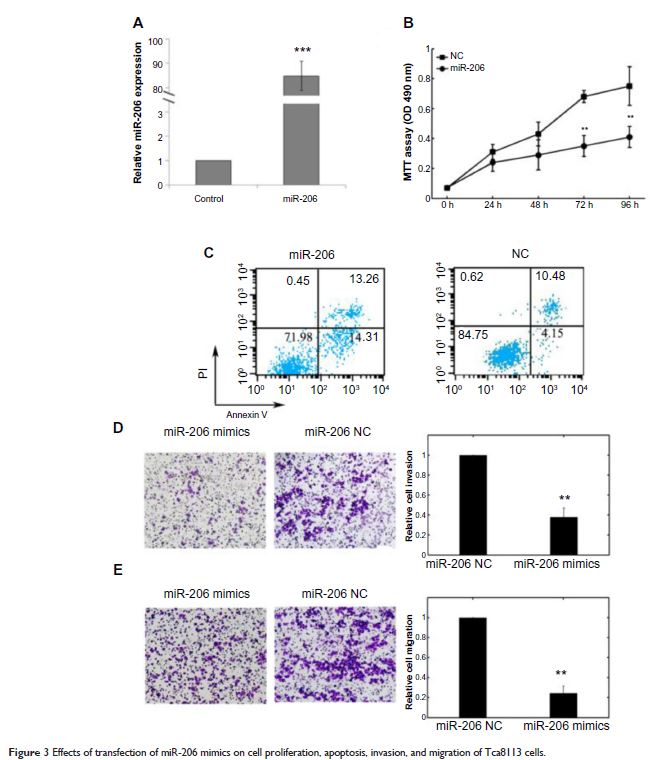
Results: MiR-206 expression was significantly downregulated in OSCC tissue samples and cell lines (both P <0.001). Decreased miR-206 expression was significantly associated with advanced tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage, advanced T classifications (ie, size and/or extent of the primary tumor), positive N classification (ie, spread to regional lymph nodes), and shorter overall survival. In addition, upregulation of miR-206 in Tca8113 cells was able to reduce cell proliferation, invasion, and migration and promote cell apoptosis in vitro. Further, K-Ras was confirmed as a direct target of miR-206 by using luciferase reporter assay.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that miR-206 may act as a tumor suppressor in OSCC and could serve as a novel therapeutic agent for miR-based therapy.
Keywords: miR-206, oral squamous cell carcinoma, prognosis, proliferation, apoptosis, invasio
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to detect miR-206 expression in OSCC cell lines and primary tumor tissues. The association of miR-206 expression with clinicopathological factors and prognosis was also analyzed. In addition, the effects of miR-206 on the biological behavior of OSCC cells were investigated. Lastly, the potential regulatory function of miR-206 on K-Ras expression was confirmed.
Results: MiR-206 expression was significantly downregulated in OSCC tissue samples and cell lines (both P <0.001). Decreased miR-206 expression was significantly associated with advanced tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage, advanced T classifications (ie, size and/or extent of the primary tumor), positive N classification (ie, spread to regional lymph nodes), and shorter overall survival. In addition, upregulation of miR-206 in Tca8113 cells was able to reduce cell proliferation, invasion, and migration and promote cell apoptosis in vitro. Further, K-Ras was confirmed as a direct target of miR-206 by using luciferase reporter assay.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that miR-206 may act as a tumor suppressor in OSCC and could serve as a novel therapeutic agent for miR-based therapy.
Keywords: miR-206, oral squamous cell carcinoma, prognosis, proliferation, apoptosis, invasio