9 8 4 6 7
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
一个新的有益于食管鳞状细胞癌患者炎症指标
Authors Feng JF, Huang Y, Chen QX
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1811—1815
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S68084
Received 21 May 2014, Accepted 21 July 2014, Published 30 September 2014
Background: The prognostic value of inflammation indexes in esophageal cancer has not been established. Recent studies have shown that the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) is a useful predictive factor. The purpose of the current study was to determine whether the ALI is useful for predicting long-term survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Patients and methods: A total of 293 patients who had undergone esophagectomy for ESCC were included. The ALI was calculated as body mass index × serum albumin/neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Then, patients were divided into two groups: ALI ≥18 and ALI <18. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to calculate the cancer-specific survival (CSS), and the difference was assessed by the log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to evaluate the prognostic factors.
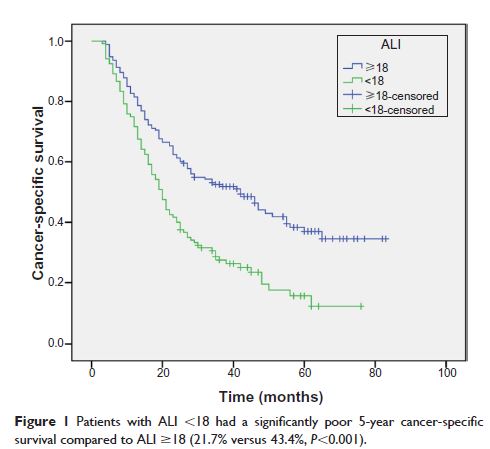
Results: In our study, there were 120 patients with ALI <18 and 173 patients with ALI ≥18. ALI was significantly higher in patients with large tumors (P =0.028), poor differentiation (P =0.010), deep invasion (P =0.009), and nodal metastasis (P =0.004). The 5-year CSS was 34.5% in our study. Patients with ALI <18 had a significantly poorer 5-year CSS compared to ALI ≥18 (21.7% versus 43.4%, P <0.001). On multivariate analysis, we showed that the ALI was a significant predictive factor of CSS (P =0.024).
Conclusion: The ALI is still a useful predictive factor for long-term CSS in patients with ESCC. However, the prognostic value of the ALI is yet to be formally tested within randomized trials.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, body mass index, albumin, survival
Patients and methods: A total of 293 patients who had undergone esophagectomy for ESCC were included. The ALI was calculated as body mass index × serum albumin/neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Then, patients were divided into two groups: ALI ≥18 and ALI <18. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to calculate the cancer-specific survival (CSS), and the difference was assessed by the log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to evaluate the prognostic factors.
Results: In our study, there were 120 patients with ALI <18 and 173 patients with ALI ≥18. ALI was significantly higher in patients with large tumors (P =0.028), poor differentiation (P =0.010), deep invasion (P =0.009), and nodal metastasis (P =0.004). The 5-year CSS was 34.5% in our study. Patients with ALI <18 had a significantly poorer 5-year CSS compared to ALI ≥18 (21.7% versus 43.4%, P <0.001). On multivariate analysis, we showed that the ALI was a significant predictive factor of CSS (P =0.024).
Conclusion: The ALI is still a useful predictive factor for long-term CSS in patients with ESCC. However, the prognostic value of the ALI is yet to be formally tested within randomized trials.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, body mass index, albumin, survival