109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
EGFR 突变作为非小细胞肺癌的一个预后与预测标志
Authors Fang S, Wang Z
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 1595—1611
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S69690
Received 19 June 2014, Accepted 17 July 2014, Published 26 September 2014
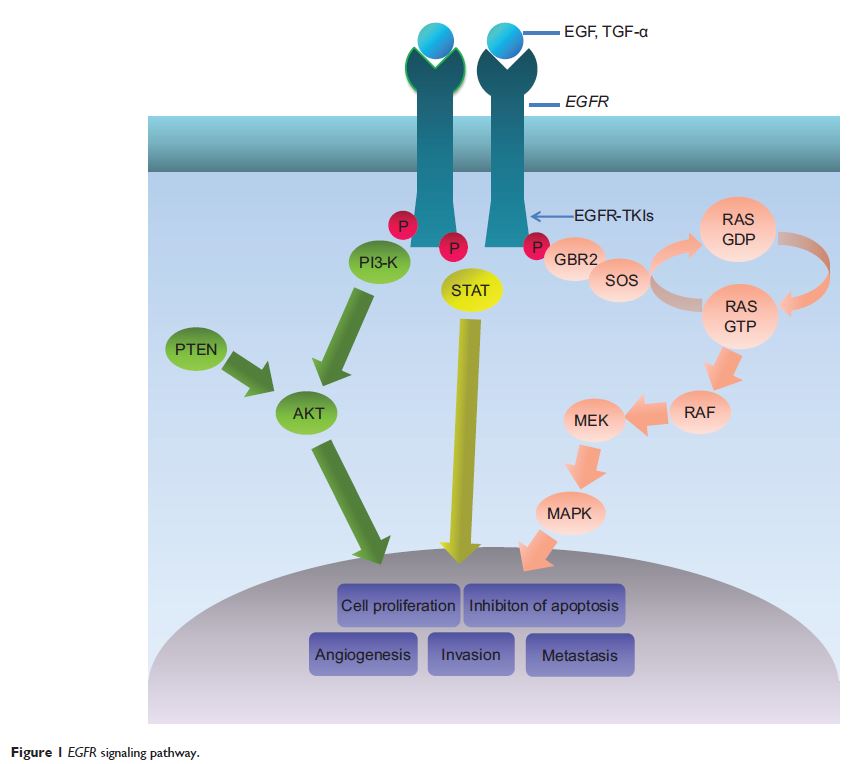
Abstract: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has entered the age of individual treatment, and increasing point mutations of specific oncogenes and rearrangement of some chromosomes are biomarkers used to predict the therapeutic effect of targeted therapy. At present, there is a consensus among clinicians that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have shown favorable efficacy in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation, and some relevant research has suggested that the presence of EGFR mutations is a favorable prognostic marker. However, the association of EGFR mutation status with the responsiveness to conventional chemotherapy agents and survival in NSCLC patients is still unclear. This review provides an overview of and assesses the role of EGFR as a prognostic marker for postoperative patients and as a predictive marker for response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. In addition, we review the comparison of response to chemotherapy between EGFR mutations in exon 19 and in exon 21 and the predictive role of p.T790M mutation.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, prediction, prognosis
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, prediction, prognosis