109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
通过 CuAAC “点击” 作为潜在的抗癌药物化学,设计、合成并制备新的抗癌活性的黄连素衍生物
Authors Jin X, Yan TH, Yan L, Li Q, Wang RL, Hu ZL, Jiang YY, Sun QY, Cao YB
Published Date August 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 1047—1059
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S63228
Received 27 February 2014, Accepted 23 April 2014, Published 6 August 2014
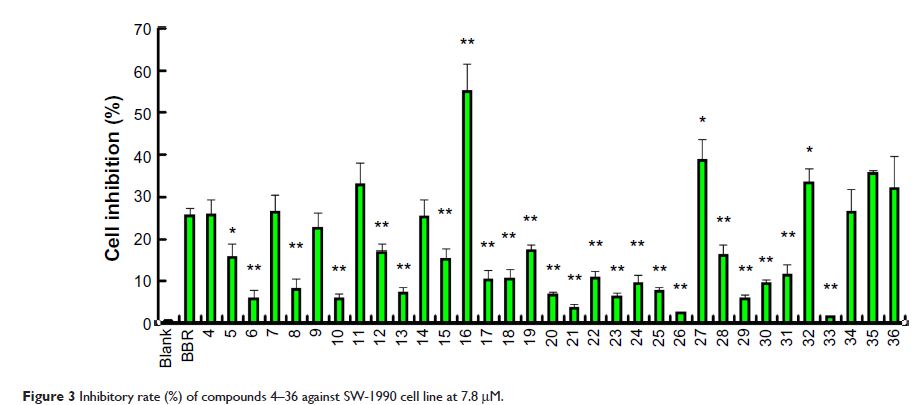
Abstract: A series of novel derivatives of phenyl-substituted berberine triazolyls has been designed and synthesized via copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition click chemistry in an attempt to develop antitumor agents. All of the compounds were evaluated for anticancer activity against a panel of three human cancer cell lines, including MCF-7 (breast), SW-1990 (pancreatic), and SMMC-7721 (liver) and the noncancerous human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) cell lines. The results indicated that most of the compounds displayed notable anticancer activities against the MCF-7 cells compared with berberine. Among these derivatives, compound 16 showed the most potent inhibitory activity against the SW-1990 and SMMC-7721 cell lines, with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 8.54±1.97 µM and 11.87±1.83 µM, respectively. Compound 36 exhibited the most potent inhibitory activity against the MCF-7 cell line, with an IC50 value of 12.57±1.96 µM. Compound 16 and compound 36 exhibited low cytotoxicity in the HUVEC cell line, with IC50 values of 25.49±3.24 µM and 30.47±3.47 µM. Furthermore, compounds 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 32, and 36 exhibited much better selectivity than berberine toward the normal cell line HUVEC.
Keywords: berberine, anticancer, click chemistry, structure–activity relationship
Keywords: berberine, anticancer, click chemistry, structure–activity relationship