109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
胡黄连苷 II 对小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用
Authors Wu N, Li W, Shu W, Jia D
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 545—554
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S62355
Received 13 February 2014, Accepted 18 March 2014, Published 14 May 2014
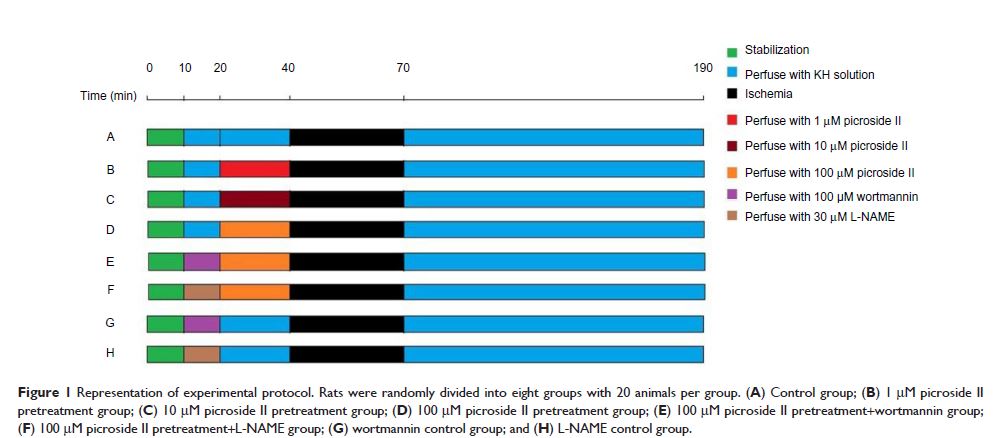
Abstract: The aim of this study was to determine the effect of picroside II on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats and to explore its underlying mechanism. Isolated rat hearts underwent 30 minutes of global ischemia followed by 120 minutes of reperfusion. Different doses of picroside II (1 µM, 10 µM, and 100 µM) were given 20 minutes before ischemia. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor (wortmannin) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor (L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester) were given 10 minutes before picroside II treatment. The cardiac function, myocardial infarct size, apoptosis, myocardial nitric oxide content, the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax, and the activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/endothelial NOS pathway were evaluated. Treatment with 10 µM and 100 µM picroside II significantly improved postischemic myocardial function, reduced myocardial infarct size, inhibited apoptosis, increased myocardial NO content, upregulated Bcl-2, downregulated Bax, and increased the phosphorylation of Akt and endothelial NOS, but cardioprotection was not shown in the 1 µM picroside II treatment group and was abrogated by wortmannin and L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester. Furthermore, cardioprotection in the 100 µM picroside II treatment group was superior to that in the 10 µM picroside II treatment group. In conclusion, the data reveals that picroside II has a significant protective effect on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in a dose-dependent manner, which was mediated by upregulating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/endothelial NOS pathway to increase nitric oxide production and regulating the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax to inhibit apoptosis.
Keywords: picroside II, ischemia reperfusion injury, apoptosis, nitric oxide, endothelial nitric oxide synthase
Keywords: picroside II, ischemia reperfusion injury, apoptosis, nitric oxide, endothelial nitric oxide synthase