109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
中国有认知的正常老龄汉族人群中,载脂蛋白 E 基因型与葡萄糖、胆固醇和甘油三酯血清水平之间的关联性
Authors Tao QQ, Chen Y, Liu ZJ, Sun YM, Yang P, Lu SJ, Xu M, Dong QY, Yang JJ, Wu ZY
Published Date July 2014 Volume 2014:9 Pages 1063—1067
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S62554
Received 16 February 2014, Accepted 18 March 2014, Published 9 July 2014
Purpose: To determine the associations between apolipoprotein E (APOE ) genotypes and serum levels of glucose, total cholesterol, and triglycerides in a cognitively normal aging Han Chinese population.
Methods: There were 1,003 cognitively normal aging subjects included in this study. APOE genotypes were analyzed and biochemical parameters were tested. All the subjects were divided into three groups according to APOE genotypes: (1) E2/2 or E2/3 (APOE E2); (2) E3/3 (APOE E3); and (3) E2/4, E3/4, or E4/4 (APOE E4). Correlations of serum levels of glucose, total cholesterol, and triglycerides with APOE genotypes were assessed.
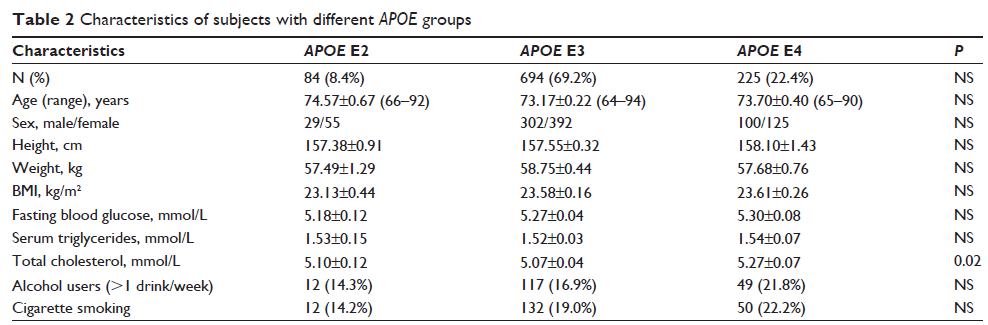
Results: E2, E3, and E4 allele frequencies were found to be 6.2%, 82.1%, and 11.7%, respectively. Serum levels of total cholesterol were higher in the APOE E4 group (P <0.05). A higher level of total cholesterol was associated with the E4 allele (adjusted odds ratio 1.689, 95% confidence interval 1.223–2.334, P <0.01). However, no association was found between APOE status and serum levels of glucose (adjusted odds ratio 0.981, 95% confidence interval 0.720–1.336, P =0.903) or total triglycerides (adjusted odds ratio 1.042, 95% confidence interval 0.759–1.429, P =0.800).
Conclusion: A higher serum level of total cholesterol was significantly correlated with APOE E4 status in a cognitively normal, nondiabetic aging population. However, there was no correlation between APOE genotypes and serum levels of glucose or total triglycerides.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, APOE , glucose level, cholesterol, triglycerides
Methods: There were 1,003 cognitively normal aging subjects included in this study. APOE genotypes were analyzed and biochemical parameters were tested. All the subjects were divided into three groups according to APOE genotypes: (1) E2/2 or E2/3 (APOE E2); (2) E3/3 (APOE E3); and (3) E2/4, E3/4, or E4/4 (APOE E4). Correlations of serum levels of glucose, total cholesterol, and triglycerides with APOE genotypes were assessed.
Results: E2, E3, and E4 allele frequencies were found to be 6.2%, 82.1%, and 11.7%, respectively. Serum levels of total cholesterol were higher in the APOE E4 group (P <0.05). A higher level of total cholesterol was associated with the E4 allele (adjusted odds ratio 1.689, 95% confidence interval 1.223–2.334, P <0.01). However, no association was found between APOE status and serum levels of glucose (adjusted odds ratio 0.981, 95% confidence interval 0.720–1.336, P =0.903) or total triglycerides (adjusted odds ratio 1.042, 95% confidence interval 0.759–1.429, P =0.800).
Conclusion: A higher serum level of total cholesterol was significantly correlated with APOE E4 status in a cognitively normal, nondiabetic aging population. However, there was no correlation between APOE genotypes and serum levels of glucose or total triglycerides.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, APOE , glucose level, cholesterol, triglycerides