109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于荧光增强金纳米粒子的 pH 响应性系统,用于肾脏靶向药物递送和纤维化治疗
Authors Lai X, Geng X, Tan L, Hu J, Wang S
Received 5 May 2020
Accepted for publication 17 July 2020
Published 6 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 5613—5627
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S260069
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
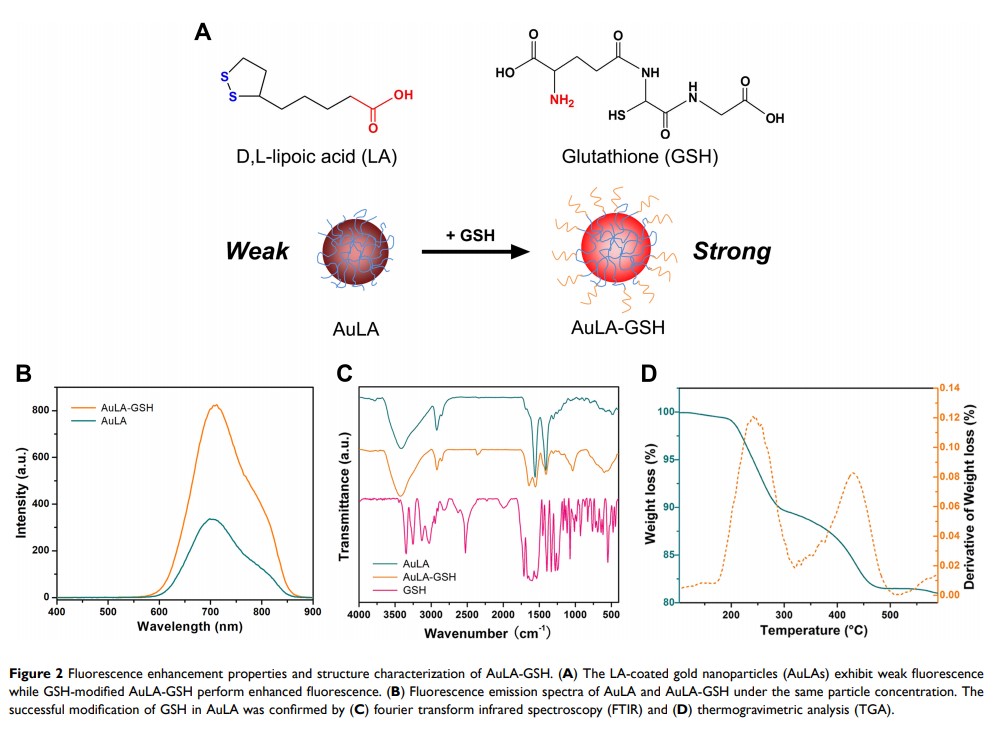
Background: Stimuli-responsive gold nano-assemblies have attracted attention as drug delivery systems in the biomedical field. However, there are challenges achieving targeted delivery and controllable drug release for specific diseases.
Materials and Methods: In this study, a glutathione (GSH)-modified fluorescent gold nanoparticle termed AuLA-GSH was prepared and a Co2+-induced self-assembly drug delivery platform termed AuLA-GSH-Co was constructed. Both the pH-responsive character and drug loading behavior of AuLA-GSH-Co were studied in vitro. Kidney-targeting capability was investigated in vitro and in vivo. Finally, the anti-fibrosis efficiency of AuLA-GSH-Co in a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) was explored.
Results: AuLA-GSH-Co was sensitive to pH changes and released Co2+ in acidic conditions, allowing it to have controllable drug release abilities. AuLA-GSH-Co was found to improve cellular uptake of Co2+ ions compared to CoCl2 in vitro. AuLA-GSH exhibited specific renal targeting and prolonged renal retention time with low non-specific accumulation in vivo. Moreover, the anti-fibrosis efficiency of AuLA-GSH-Co was higher compared to CoCl2 in a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO).
Conclusion: AuLA-GSH-Co could greatly enhance drug delivery efficiency with renal targeting capability and obviously relieve renal fibrosis, providing a promising strategy for renal fibrosis therapy.
Keywords: gold nanoparticles, self-assembly, pH sensitivity, drug delivery, renal fibrosis