109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血清外泌体 miR-1290 是肺腺癌的潜在生物标志物
Authors Wu Y, Wei J, Zhang W, Xie M, Wang X, Xu J
Received 27 May 2020
Accepted for publication 19 July 2020
Published 5 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7809—7818
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S263934
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
Purpose: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death, with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) representing the most common subtype. Recently, exosome-based biomarkers have provided new diagnostic approaches for malignancies. We aimed to identify specific exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) as noninvasive biomarkers for LUAD.
Patients and Methods: A total of 110 participants were enrolled and randomly divided into two sets: the discovery set (n=20) and the validation set (n=90). Exosomes were isolated from serum, and miRNAs were subsequently extracted. Candidate miRNAs (miR-21, miR-221-3p, miR-222-3p, miR-223, miR-638 and miR-1290) were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) in the discovery set. The upregulated miR-1290 was then selected for further analysis in the validation set along with three tumor markers (CEA, CYFRA21-1 and NSE). The diagnostic and prognostic value of exosomal miR-1290 were estimated through receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) and survival analysis.
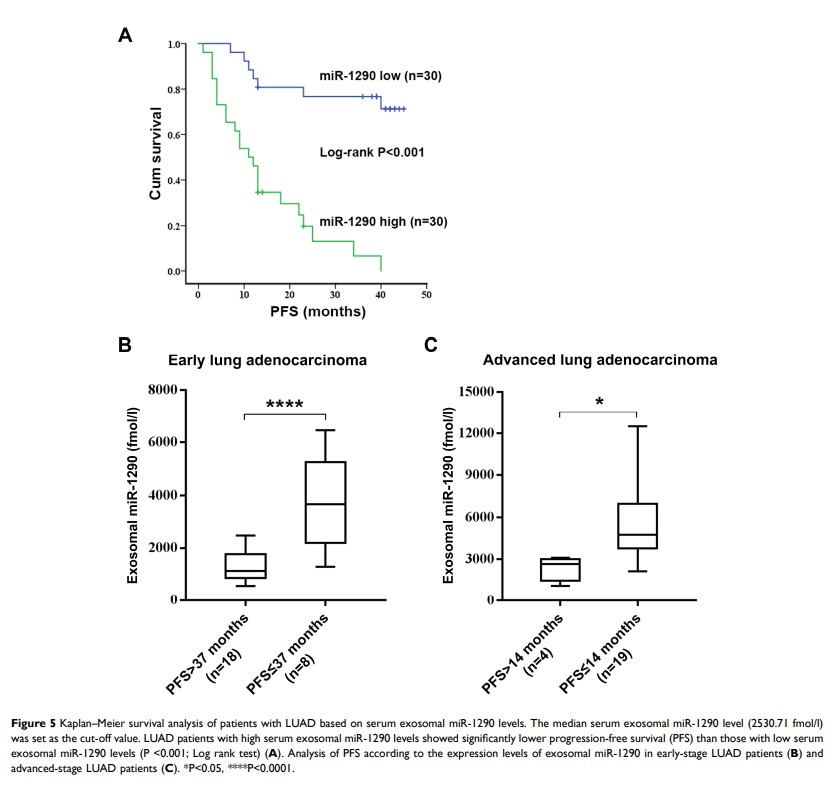
Results: Serum exosomal miR-1290 was significantly upregulated in LUAD patients compared to healthy controls (P< 0.001) and decreased after resection (P=0.0029). Its expression level was associated with tumor stage, tumor size, lymph node and distant metastasis (all P < 0.05). Exosomal miR-1290 had a higher diagnostic efficacy than CEA, CYFRA21-1 and NSE, with a sensitivity of 80.0% and specificity of 96.7% (AUC: 0.937, 95% CI: 0.890– 0.985; P< 0.001). Moreover, LUAD patients with a high level of exosomal miR-1290 had significantly poorer progression-free survival (PFS) than those with a low level of exosomal miR-1290 (mean PFS: 14 months vs 37 months, P< 0.001). Cox proportional hazards model analysis demonstrated that exosomal miR-1290 could be an independent risk factor for the prognosis of LUAD (HR=7.80, P=0.017).
Conclusion: Serum exosomal miR-1290 could be a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for LUAD.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, circulating miRNA, exosome, biomarker