109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA MAFG-AS1 通过 miR-765/PDX1 轴加速食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的迁移、侵袭和有氧糖酵解
Authors Qian C, Xu Z, Chen L, Wang Y, Yao J
Received 12 May 2020
Accepted for publication 22 July 2020
Published 5 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6895—6908
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S262075
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
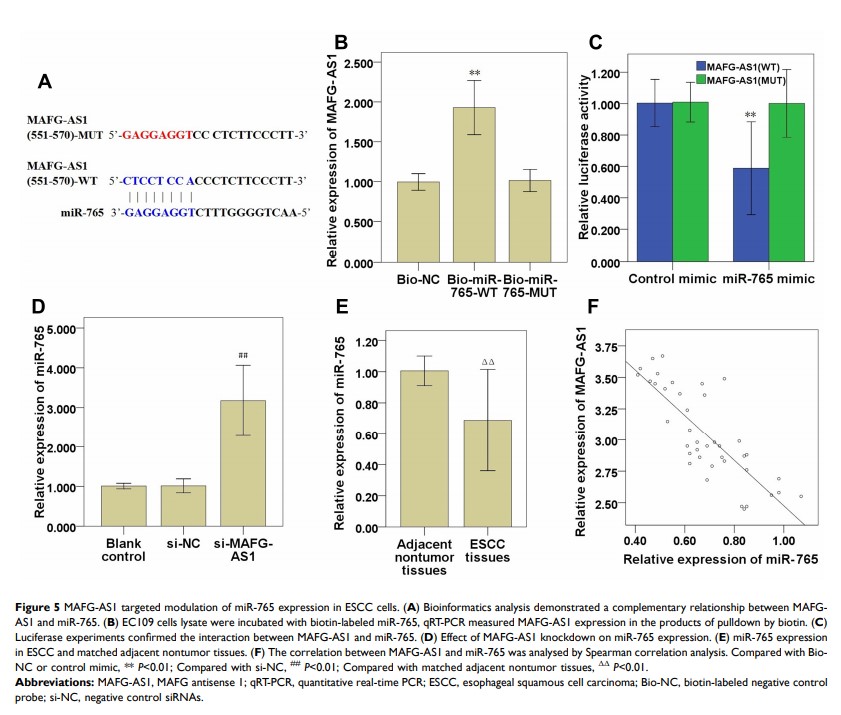
Background: LncRNA dysregulation is implicated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression; However, the precise role and function of lncRNA MAFG-AS1 in ESCC remains unknown.
Materials and Methods: Expressions of MAFG-AS1, miR-765, PDX1, GLUT1 and LDH-A were detected via qRT-PCR or/and Western blot in ESCC tissues and cell lines. CCK-8, transwell and glycolysis assays were used to investigate the effects of MAFG-AS1 on ESCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and aerobic glycolysis after knockdown or overexpression of MAFG-AS1, and bioinformatics analyses, RNA pull-down and dual luciferase reporter systems were applied to investigate the interaction between MAFG-AS1, miR-765 and PDX1.
Results: MAFG-AS1 was significantly up-modulated in ESCC tissues and cell lines. MAFG-AS1 significantly accelerated ESCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and aerobic glycolysis. MAFG-AS1 competitively adsorbed miR-765, while miR-765 negatively modulated the expression of PDX1. miR-765 and PDX1 participated in the promotive effects of MAFG-AS1 on cell migration, invasion and aerobic glycolysis in ESCC cells.
Conclusion: Our research indicates that the MAFG-AS1/miR-765/PDX1 axis accelerates ESCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and aerobic glycolysis.
Keywords: ESCC, MAFG-AS1, aerobic glycolysis, miR-765, PDX1