109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circ_0136666 通过 miR-383/CREB1 轴促进结直肠癌的进展
Authors Li Y, Zang H, Zhang X, Huang G
Received 29 February 2020
Accepted for publication 9 July 2020
Published 4 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6795—6806
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S251952
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: The changes in dietary patterns cause an increased incidence of colorectal cancer (CRC) globally. We aimed to explore the mechanism behind circular RNA circ_0136666 in the progression of CRC.
Materials and Methods: The expression of circ_0136666, miR-383 and cAMP response element binding protein 1 (CREB1) was detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Cell proliferation, apoptosis and glycolysis were measured by 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), flow cytometry and glucose or lactate detection kit, respectively. The combination between miR-383 and circ_0136666 or CREB1 in 293T cells was predicted by Circular RNA Interactome or Starbase software and confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Western blot assay was performed to detect the abundance of CREB1, hexokinase 2 (HK2) and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) in CRC cells. Murine xenograft model was established to verify the function of circ_0136666 in vivo.
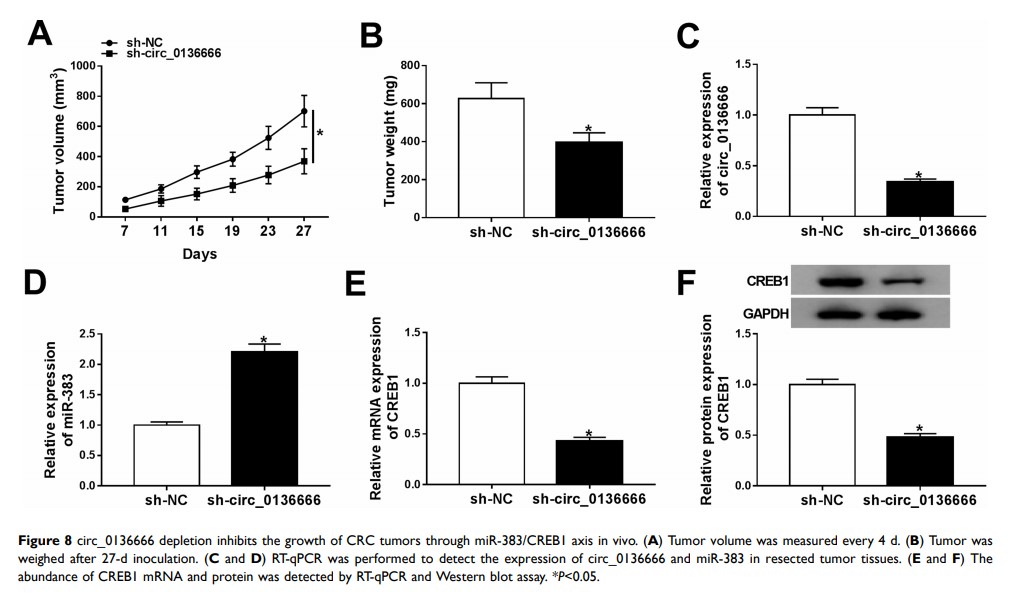
Results: circ_0136666 was aberrantly up-regulated in CRC tissues and cells, and it promoted the proliferation and glycolysis and inhibited the apoptosis of CRC cells. circ_0136666 accelerated the progression of CRC through directly targeting and down-regulating miR-383. CREB1 could bind to miR-383 in 293T cells. The overexpression of CREB1 reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-383 accumulation on the proliferation and glycolysis and the promoting impact on the apoptosis of CRC cells. The enrichment of CREB1 was modulated by circ_0136666/miR-383 signaling in CRC cells. The glycolysis-related proteins (HK2 and LDHA) were modulated by circ_0136666/miR-383/CREB1 axis in CRC cells. circ_0136666 accelerated the growth of CRC tumors via circ_0136666/miR-383/CREB1 axis in vivo.
Conclusion: circ_0136666 deteriorated CRC through miR-383/CREB1 axis. circ_0136666/miR-383/CREB1 axis might be an underlying therapeutic target for CRC therapy.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, circ_0136666, miR-383, CREB1, proliferation, apoptosis, glycolysis