109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA LINC00460 通过负调节 miR-613 促进大肠癌进展
Authors Wang L, Chen X, Sun X, Suo J
Received 18 March 2020
Accepted for publication 15 July 2020
Published 3 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7555—7569
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S254489
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: Long-noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) could exert a crucial effect on the development of human cancers, including CRC. However, the biological function and underlying mechanism of LINCRNA00460 in the development of CRC still need deeper exploration.
Materials and Methods: The expression of LINC00460 in CRC tissues and cell lines was assessed by qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were measured by the respective cell counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), wound healing assay and transwell invasion assay. Cell apoptosis and caspase-3 activity were detected by flow cytometry and caspase-3 activity assay. The relationship between LINC00460 and miR-613 expression was explored by Dual-luciferase reporter assay. Protein expression was measured by Western blotting. In vivo tumour growth was evaluated using a xenograft model of nude mice.
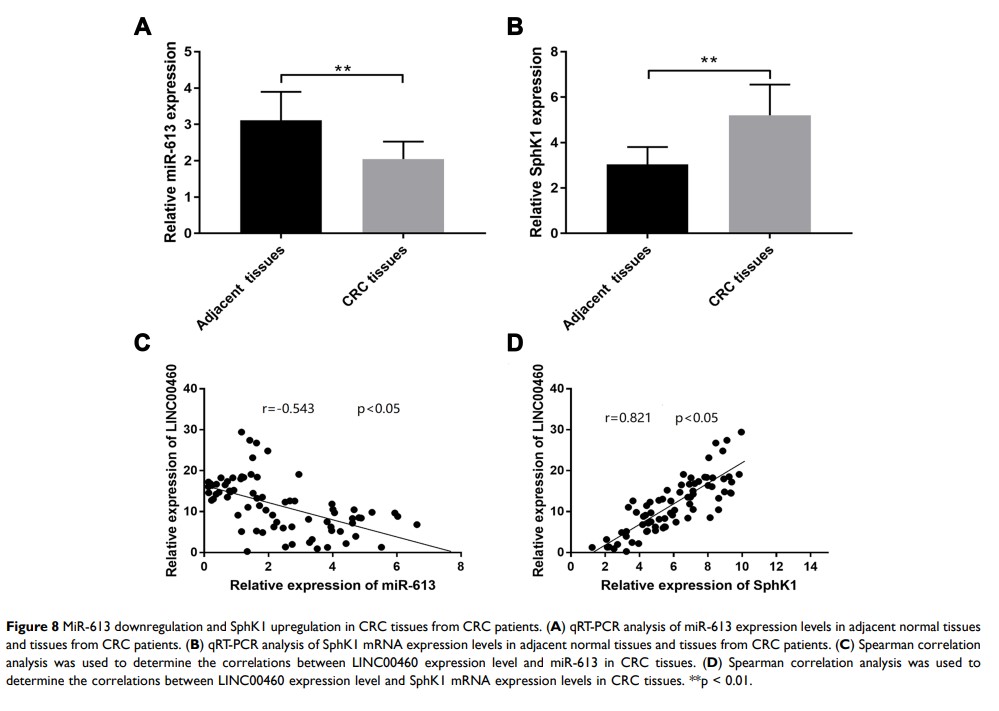
Results: LINC00460 was markedly up-regulated in CRC tissues and cell lines compared to their corresponding controls, which was closely correlated with clinical stage, TNM (T) classification, nodal (N) classification, metastasis (M) classification, liver metastasis and pathological differentiation, and survival rate of CRC patients. Functionally, LINC00460 knockdown decreased the proliferative, migrative and invasive abilities, and enhanced apoptosis rates and caspase-3 activity in HT29 and LOVO cells. Mechanistic studies indicated that miR-613 was targeted by LINC00460 , and SphK1 was targeted and inversely regulated by miR-613 in HT29 and LOVO cells. In vivo studies, LINC00460 knockdown attenuated tumour growth. MiR-613 downregulation and SphK1 upregulation in the CRC tissues, and LINC00460 expression levels were inversely correlated with miR-613 expression and positively correlated with the SphK1 mRNA expression. Overall, LINC00460 modulated cell proliferation, migration, invasion and sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) expression in HT29 and LOVO cells, at least in most part, by regulating miR‐613.
Conclusion: LINC00460 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate SphK1 expression by sponging miR‐613 in CRC and provides a valuable therapeutic strategy for CRC patients.
Keywords: long noncoding RNA 00460, miR‐613, colorectal cancer, SphK1