109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LanCL1 过表达的前列腺癌细胞中的关键信号通路和中枢基因的确定
Authors Tang R, Wu Z, Lu F, Wang C, Wu B, Wang J, Zhu Y
Received 8 March 2020
Accepted for publication 15 July 2020
Published 3 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7653—7664
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S252958
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies in urology, especially in developed countries. Our previous studies showed that Lanthionine synthase C-like protein 1 (LanCL1 ) can promote the proliferation of prostate cancer cells and protect cells from oxidative stress. Also, LanCL1 protects cells by inhibiting the JNK signaling pathway after H2O2 treatment.
Materials and Methods: In our study, we analyzed the data of RNA-seq to identify the DEGs after LanCL1 overexpression. We performed a functional enrichment analysis with gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and a database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery (DAVID). We also identified the critical hub gene correlated with disease prognosis by Cox regression analysis.
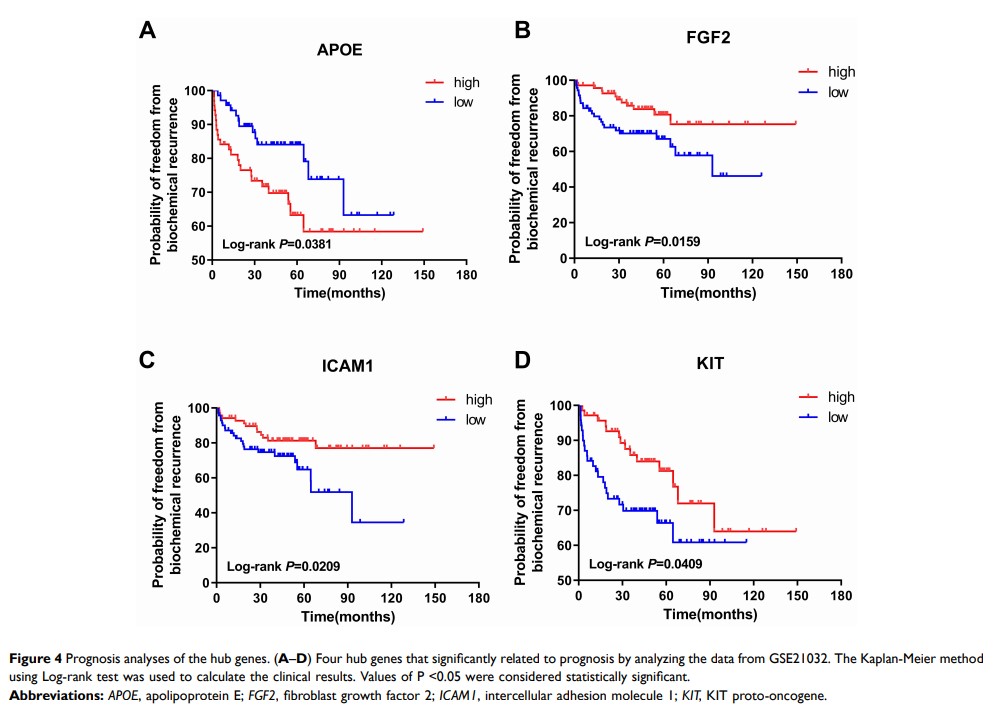
Results: A total of 8928 DEGs were identified. Through the analysis of GO and KEGG, we found that DEGs are significantly enriched in categories related to metabolism, cancer-related signaling pathways, and inflammation. The top 15 hub genes were then identified and ranked by degree from the protein–protein interaction network. Survival analysis showed 4 hub genes related to disease prognosis and ICAM1 expression is an independent risk factor for the prognosis.
Conclusion: Our results suggest the critical genes and pathways that might play key roles after LanCL1 overexpression in prostate cancer. We also provide candidate gene targets that might play important roles in prostate cancer development.
Keywords: prostate cancer, RNA sequencing, LanCL1