109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

急性白血病和髓系肿瘤中的 SET-CAN 融合基因:一份三病例报告和文献综述
Authors Zhang H, Zhang L, Li Y, Gu H, Wang X
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 17 July 2020
Published 3 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7665—7681
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S258365
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Objective: To investigate the characteristics of hematological malignancies in patients with the SET-CAN fusion gene and provide a literature review.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of three cases of acute leukemia and myeloid neoplasms harboring the SET-CAN fusion gene who were treated at our hospital. Their clinical manifestations, pathological results and treatment strategies were investigated.
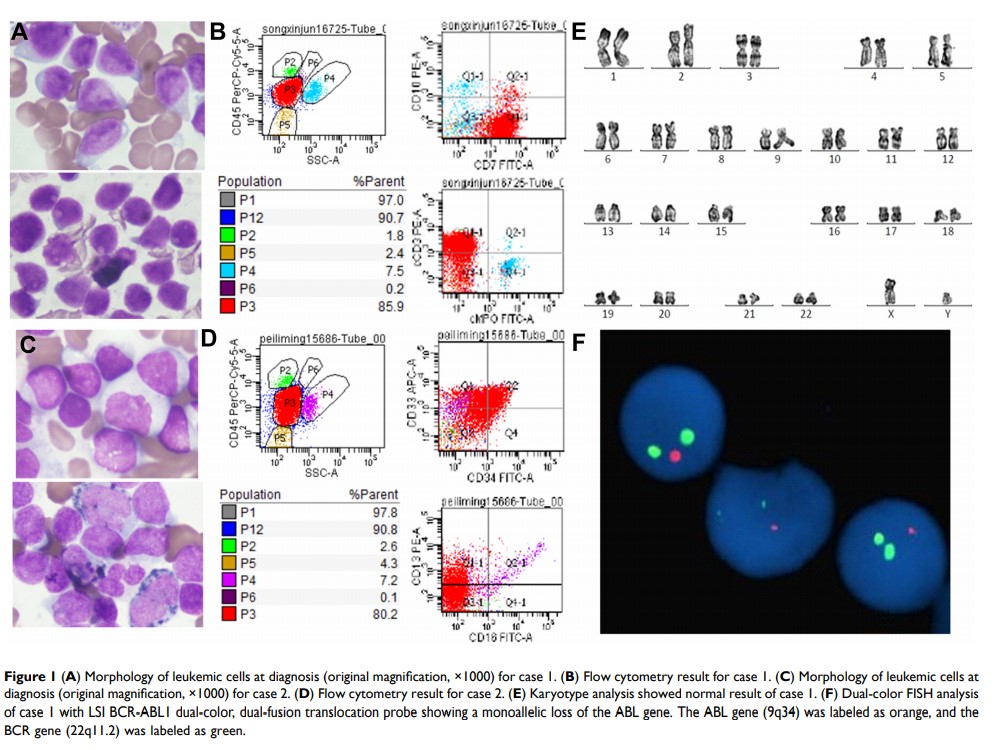
Results: The three cases were diagnosed with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myeloid sarcoma (MS), respectively. Karyotype analyses identified a normal result in all three patients. Subsequently, we confirmed del(9q34) utilizing FISH analysis. Mutation of the BRAF gene was detected in case 1, while mutations in PHF6 and BCOR were detected in case 2, which have not been officially reported in patients with SET-CAN fusions. Finally, relevant literature focusing on adult patients with hematological malignancies harboring the SET-CAN fusion gene were summarized.
Conclusion: Adult patients with the SET-CAN fusion gene were rare among cases of hematological malignancies. There was a large degree of heterogeneity between different patients. Notably, some patients remained sensitive to chemotherapy. Overall prognosis may be related to the type of disease and other cytogenetic abnormalities. Systemic cytogenetic and molecular studies are needed to make accurate diagnoses. Additional cases need to be accumulated and summarized to better understand these diseases.
Keywords: T-lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, myeloid sarcoma, SET-CAN , ASCT, prognosis