109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

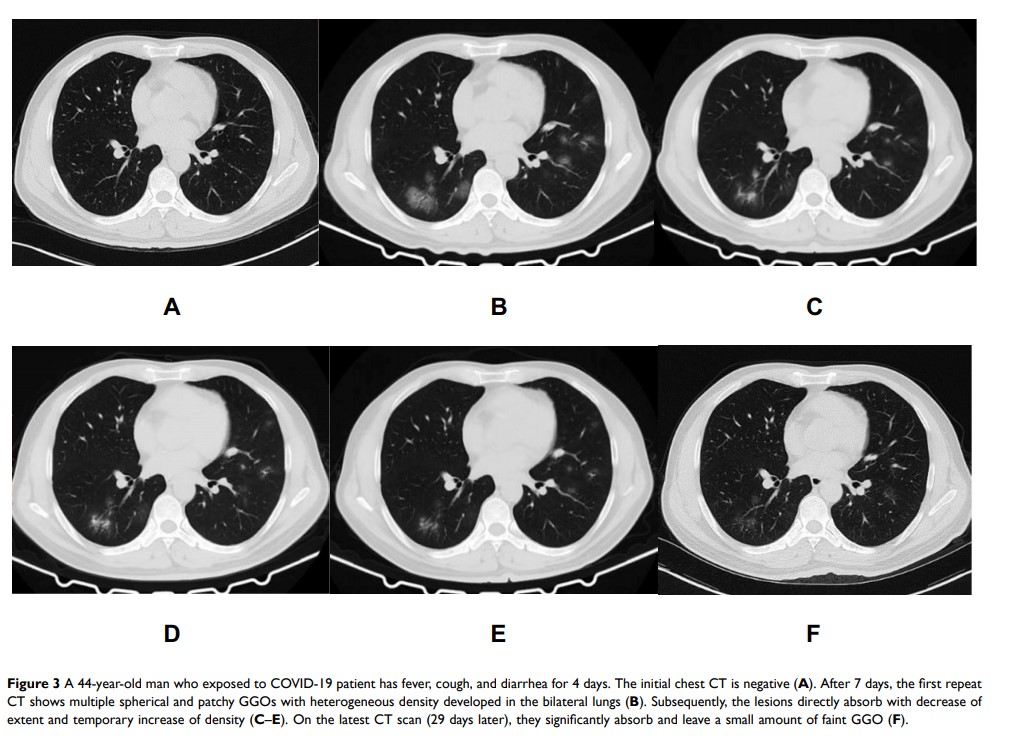
初始胸部 CT 为阴性的 COVID-19 患者的随访 CT 结果
Authors Fu B, Hu L, Lv F, Huang J, Li W, Ouyang Y, Chu Z
Received 22 April 2020
Accepted for publication 16 July 2020
Published 3 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2681—2687
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S258677
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Purpose: To determine whether new pulmonary lesions will develop in COVID-19 patients with negative initial chest CT findings and to investigate their CT features and outcome during treatment.
Patients and Methods: Data were collected retrospectively from 29 patients who had tested positive for COVID-19 by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction testing but negative by initial chest CT from January 22 to February 17, 2020. Clinical manifestations, laboratory indicators, and follow-up CT data were evaluated.
Results: Among 317 confirmed COVID-19 patients, 29 (9.1%) (mean ± SD, 38.5 ± 20.5 years; 12 women) with negative initial chest CT findings were evaluated. New pulmonary lesions developed in 10 (34.5%) patients on follow-up CT. Mean time from onset of new lesions to initial CT was 5.8 ± 3.0 days (range: 2– 12 days). New lesions (mean involved lobes and segments: 2.5 ± 1.6 [range: 1– 5] and 4.5 ± 4.5 [range: 1– 13]) were mainly spherical/patchy ground-glass opacities frequently located in the left lower lobe (9, 90.0%). Among the 10 patients, lesions in 6 (60.0%) indicated progression after occurrence, and those in 10 (100.0%) indicated significant absorption on latest CT. When new lesions developed, 6 (60.0%) patients developed new symptoms or had aggravated symptoms and 3 (30.0%) had decreased lymphocyte count. Patients with worsening symptoms had higher involvement of lung segments (mean: 6.5 ± 5.0, range: 1– 13) than asymptomatic patients (mean: 1.5 ± 0.6, range: 1– 2) (P = 0.057).
Conclusion: In COVID-19 patients with negative initial chest CT findings, new pulmonary lesions may develop during treatment. Repeat CT is necessary for monitoring the disease, especially when patients have worsening symptoms or laboratory indicators.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019, SARS-CoV-2, follow-up, CT imaging