109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

分析 DNA 甲基化参与核转运蛋白 α2 活化对人乳腺癌进展和预后的意义
Authors Cui X, Jing X, Wu X, Xu J, Liu Z, Huo K, Wang H
Received 15 May 2020
Accepted for publication 13 July 2020
Published 3 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6665—6677
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S261290
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
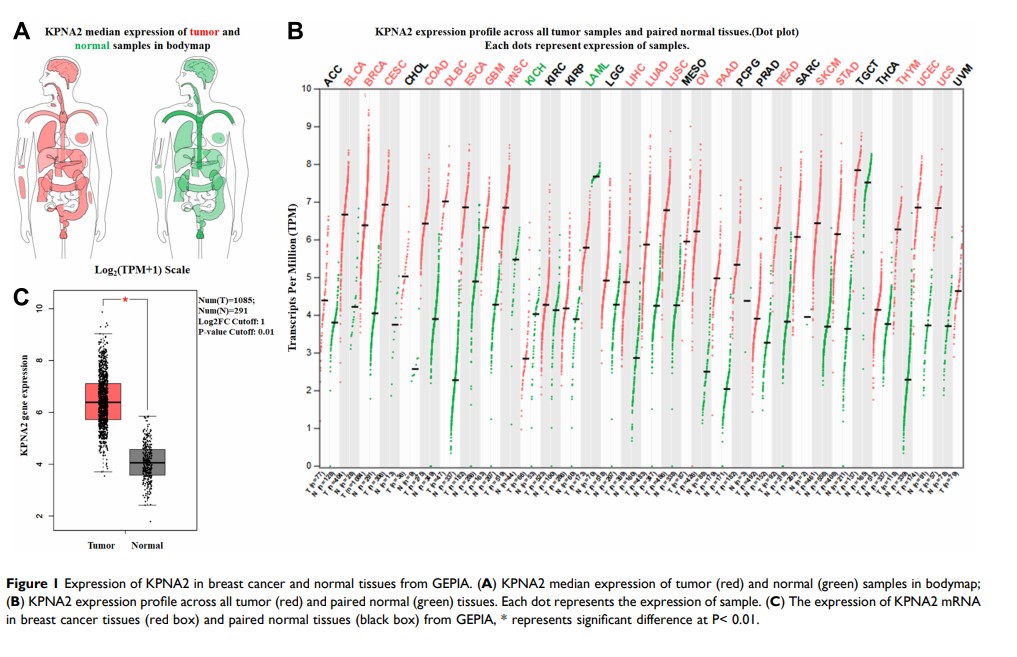
Background: Karyopherin alpha 2 (KPNA2) is a nuclear import factor that plays a crucial role in nucleocytoplasmic transport, as well as cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in several cancers. However, the roles of KPNA2 in breast cancer as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been elucidated.
Materials and Methods: To evaluate gene expression alterations during breast carcinogenesis, KPNA2 expression was analyzed using the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis and Oncomine analyses. The correlation between methylation and expression was analyzed using the MEXPRESS tool, UALCAN cancer database, and cBioPortal browser. Then, the expression and prognostic value of KPNA2 were investigated by our own breast cancer samples using RT-PCR. KPNA2 methylation level was detected by methylation-specific PCR.
Results: We obtained the following important results. (1) KPNA2 expression was significantly higher in breast cancer than normal samples and regulated by aberrant DNA hypomethylation of promoter region. (2) Among patients with breast cancer, those with higher KPNA2 expression had a lower survival rate. (3) The major mutation type of KPNA2 in breast cancer samples was missense mutation. (4) Homer1 was able to promote breast cancer progression may be through upregulating TPX2 expression.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that aberrant DNA hypomethylation of promoter regions contributes to the aberrant expression of KPNA2 in breast cancer, which might be a potential indicator of poor prognosis.
Keywords: KPNA2, breast cancer, prognosis, methylation, TPX2