109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

甲基化和拷贝数变异均参与了多发性骨髓瘤中 PRAME 的各种表达
Authors Yang L, Dao FT, Chang Y, Wang YZ, Li LD, Chen WM, Long LY, Liu YR, Lu J, Liu KY, Qin YZ
Received 3 December 2019
Accepted for publication 3 July 2020
Published 31 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7545—7553
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S240979
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Purpose: The cancer-testis antigen, which is a preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma (PRAME), is an ideal target for immunotherapy and cancer vaccines. Since the expression of this antigen is relevant to therapy responses, the heterogeneity in its expression and the underlying mechanism need to be investigated.
Patients and Methods: Plasma cell sorting was performed in 48 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) patients. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed to examine the PRAME transcript levels and gene copy numbers. Bisulfate clone sequencing of the PRAME promoter and exon 1b regions was performed in 4 patients. Quantitative methylation-specific PCR of the +287 CpG site was performed for all patients. The human MM cell lines RPMI8226, LP-1 and MOLP-2 were treated with 5-azacytidine.
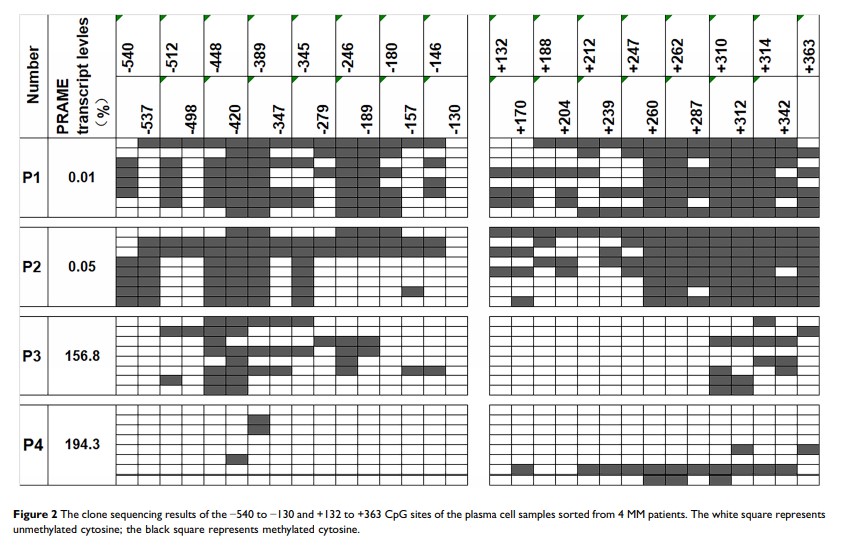
Results: The median PRAME transcript level was 3.1% (range: 0– 298.3%) in the plasma cells sorted from the 48 MM patients. Eleven (22.9%) and 37 (77.1%) patients were individually categorized into the PRAME low- and high-expression groups according to the cut-off value of 0.05%. The methylation ratios of the promoter and the 3ʹ region of exon 1b region were both negatively related to the transcript levels. The degrees of methylation at the +287 CpG site were significantly negatively related to the transcript levels in all 48 patients (r=− 0.44, P=0.0018), and those in the high-expression group (r=− 0.69, P< 0.0001) but not those in the low-expression group (r=− 0.27, P=0.43). All 5 patients with homozygous deletions were categorized into the low-expression group. There were no significant differences in the PRAME transcript levels between the hemizygous deletion (n=8) and no deletion (n=35) groups (P=0.40). Furthermore, the PRAME transcript levels significantly increased in the MM cell lines after treatment with 5-azacytidine.
Conclusion: Both methylation and copy number variation may participate in the regulation of PRAME expression in MM; in patients with no homozygous deletion, PRAME expression is mainly controlled by methylation, and a proportion of fairly low expression is caused by homozygous deletion.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma, PRAME, gene methylation, gene copy number variation