109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-31-5p 通过 PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 信号通路调节 14-3-3ɛ ,从而抑制前列腺癌 22RV1 细胞的存活和增殖
Authors Zhao J, Xu H, Duan Z, Chen X, Ao Z, Chen Y, Ruan Y, Ni M
Received 30 January 2020
Accepted for publication 3 July 2020
Published 31 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6679—6694
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S247780
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Introduction: Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most common malignancies, and almost all patients with advanced PCa will develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) after receiving endocrine therapy. Effective treatment for patients with CRPC has not been established. Novel approaches are needed to identify therapeutic targets for CRPC.
Purpose: Recent research studies have found that members of the 14-3-3 family play an important role in the development and progression of PCa. Previous results have shown that 14-3-3 ɛ is significantly upregulated in several cancers. This study aimed to identify novel miRNAs that regulate 14-3-3 ɛ expression and therapeutic targets for CRPC.
Methods: In this study, we used computation and experimental approaches for the prediction and verification of the miRNAs targeting 14-3-3 ɛ, and investigated the potential roles of 14-3-3 ɛ in the survival and proliferation of 22RV1 cells.
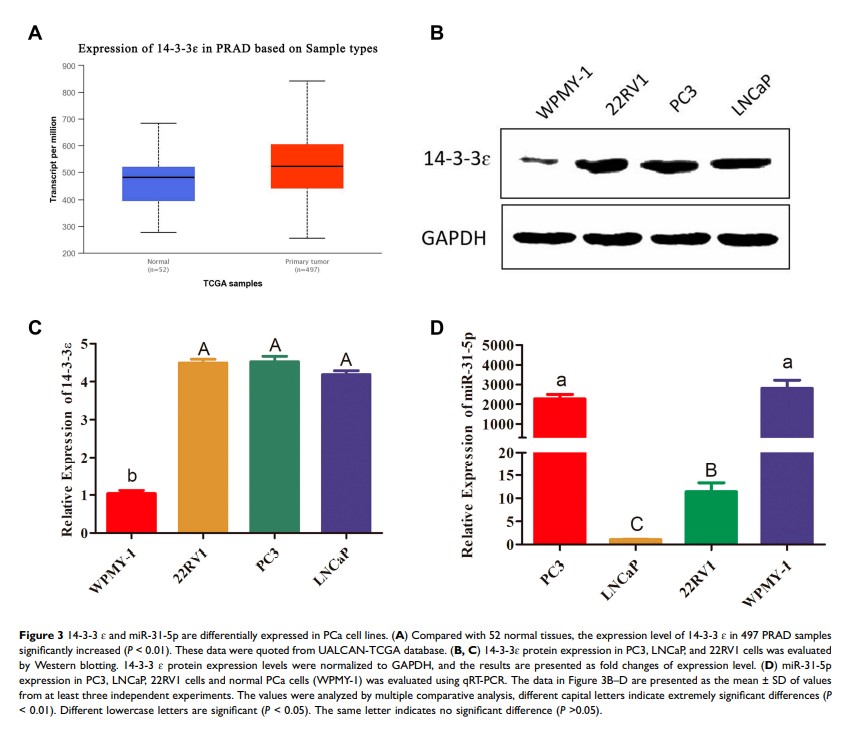
Results: We confirm that mir-31-5p is downregulated in 22RV1 cells and acts as a tumor suppressor by regulating 14-3-3 ɛ . Ectopic expression of miR-31-5p or 14-3-3 ɛ interference significantly inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in 22RV1 cells, as well as promotes cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Moreover, 14-3-3 ɛ is required for the miR-31-5p-mediated upregulation of the PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our findings provide information on the underlying mechanisms of miR-31-5p/ 14-3-3 ɛ in 22RV1 cell proliferation and apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. These results suggest that miR-31-5p and 14-3-3 ɛ may potentially be utilized as novel prognostic markers and therapeutic targets for PCa treatment.
Keywords: prostate cancer, miR-31-5p, 14-3-3 ϵ , PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway, cell proliferation, cell apoptosis