109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小白菊内酯通过抑制 VEGF 来遏制食管鳞状细胞癌的血管生成
Authors Tian B, Xiao Y, Ma J, Ou W, Wang H, Wu J, Tang J, Zhang B, Liao X, Yang D, Wu Z, Li X, Zhou Y, Su M, Wang W
Received 31 March 2020
Accepted for publication 2 July 2020
Published 29 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7447—7458
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S256291
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Parthenolide (PT), the effective active ingredient of the medicinal plant, feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium ), has been used as an anti-inflammatory drug due to its involvement in the inhibition of the NF-кB pathway. Moreover, recent studies have demonstrated the anti-tumor effect of PT in several cancers. However, the effect of PT on esophageal carcinoma remains unclear to date. In this study, we examined the inhibitory effects of PT and its underlying mechanism of action in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells – Eca109 and KYSE-510.
Methods: The proliferation ability of Eca109 and KYSE-510 treated with PT was detected using the Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony forming assay. The Transwell assay and the wound healing assay were used to analyze the cell invasion and migration ability, respectively. The tube formation assay was used to investigate the effect of PT on tube formation of endothelial cells. The expression level of NF-кB, AP-1 and VEGF was analyzed by Western blot.
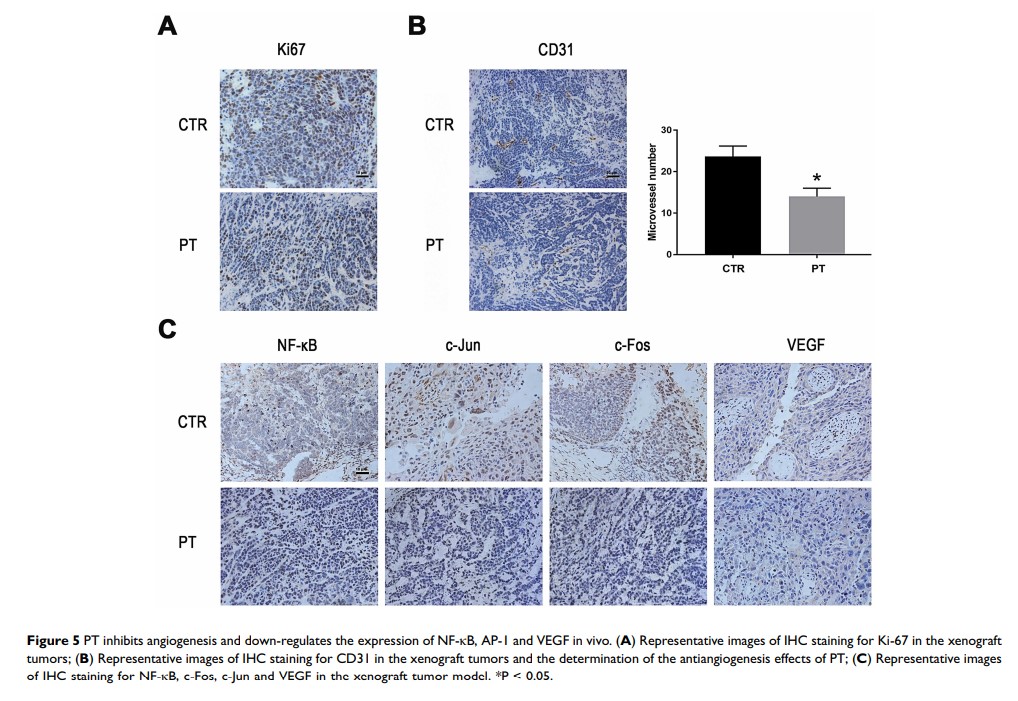
Results: We demonstrated that PT attenuates the proliferation and migration ability of ESCC cells in vitro and also inhibits tumor growth in the mouse xenograft model. In addition, PT exhibited anti-angiogenesis activity by weakening the proliferation, invasion and tube formation of endothelial cells in vitro and reduced microvessel density in the xenograft tumors. Further studies revealed that PT reduced the expression level of NF-кB, AP-1 and VEGF in ESCC cells.
Conclusion: Collectively, the results of our study demonstrated that PT exerts anti-tumor and anti-angiogenesis effects possibly by inhibiting the NF-кB/AP-1/VEGF signaling pathway on esophageal carcinoma and might serve as a promising therapeutic agent for ESCC.
Keywords: parthenolide, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, NF-кB, VEGF, AP-1