109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

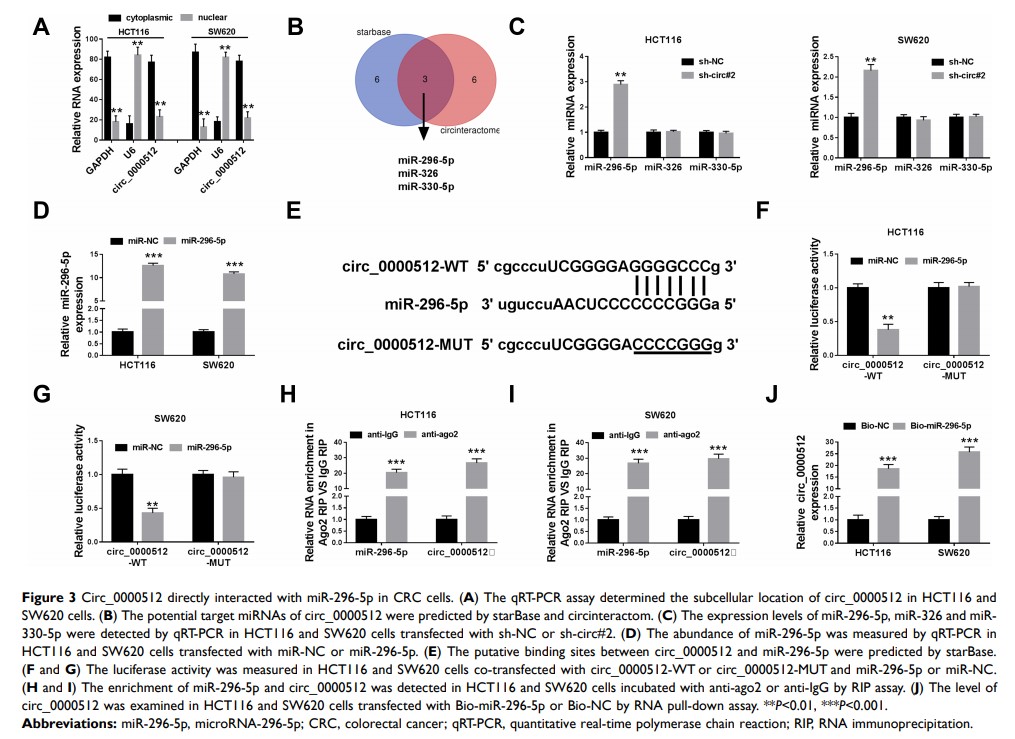
敲低 circ_0000512 可通过调节 miR-296-5p/RUNX1 轴,抑制结直肠癌的细胞增殖并促进细胞凋亡
Authors Wang L, Wu H, Chu F, Zhang L, Xiao X
Received 19 February 2020
Accepted for publication 3 July 2020
Published 28 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7357—7368
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S250495
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide. Increasing evidence showed that circular RNAs (circRNAs) played critical roles in the progression of CRC. However, the effects and underlying mechanisms of circ_0000512 in CRC progression remain unclear.
Methods: The expression levels of circ_0000512, microRNA-296-5p (miR-296-5p) and runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) were analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell viability, colony formation, cell cycle distribution and cell apoptosis were detected by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, colony formation assay and flow cytometry analysis, respectively. Western blot assay was utilized to measure the protein expression of Cyclin D1, Cleaved Caspase-3 and RUNX1. The interaction between miR-296-5p and circ_0000512 or RUNX1 was predicted by starBase and verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay and RNA pull-down assay. The mice xenograft model was established to explore the function of circ_0000512 in vivo.
Results: The expression of circ_0000512 was increased in CRC tissues and cells. Knockdown of circ_0000512 suppressed cell viability and colony formation and arrested the cells at the G0/G1 phase while it accelerated apoptosis in CRC cells. Mechanistically, circ_0000512 could increase RUNX1 expression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-296-5p in CRC cells. Furthermore, miR-296-5p downregulation or RUNX1 overexpression reversed the anti-proliferation and pro-apoptosis effects caused by circ_0000512 knockdown in CRC cells. In addition, circ_0000512 interference inhibited tumor growth by upregulating miR-296-5p and downregulating RUNX1 in vivo.
Conclusion: Knockdown of circ_0000512 inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in CRC cell by regulating miR-296-5p/RUNX1 axis, which might provide a potential therapeutic target for CRC treatment.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, circ_0000512, -miR-296-5p, RUNX1, proliferation, apoptosis