109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过生物信息学分析和体外实验,FKBP10 可成为胃癌预后和淋巴结转移的新生物标志物
Authors Gong LB, Zhang C, Yu RX, Li C, Fan YB, Liu YP, Qu XJ
Received 9 March 2020
Accepted for publication 19 June 2020
Published 28 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7399—7409
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S253154
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Purpose: To explore the role of FKBP prolyl isomerase 10 (FKBP10 ) protein in the progression of gastric cancer.
Methods: Four independent gastric cancer databases (GSE27342, GSE29272, GSE54129 and TCGA-STAD) were used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis was used to identify the abnormally active pathways in patients with gastric cancer. Univariate Cox regression analysis was used to identify genes with stable prognostic value in gastric cancer patients based on three independent gastric cancer databases (GSE15459, GSE62254, TCGA-STAD). Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to explore the possible pathways related to FKBP10 . The reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was employed to determine the expression of FKBP10 mRNA in the HGC-27 and MKN-7 cell lines. Adhesion assay was used to detect changes in cell adhesion ability. FKBP10 , ITGA1 , ITGA2 , ITGA5 , ITGAV , ITGA6 , P-AKT 473, P-AKT 308, AKT , and β-actin were evaluated by Western blot (WB).
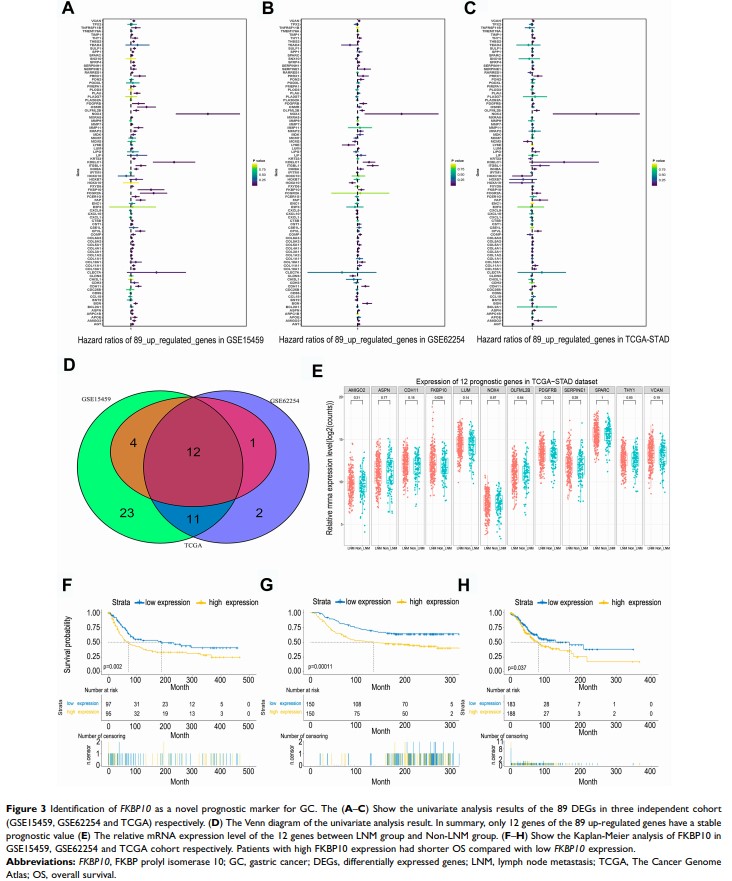
Results: We first performed differential expression genes (DEGs) screening of four independent GC databases (GSE27342, GSE29272, GSE54129 and TCGA-STAD). Eighty-nine genes showed consistent up-regulation in GC, the results of pathway analysis showed that they were related to “Focal adhesion”. The prognostic value of these 89 genes was tested in three independent GC databases GSE15459, GSE62254 and TCGA-STAD cohort. Finally, 12 genes, in which the expression of FKBP10 was prominently increased in patients with lymph node metastasis (LNM), showed stable prognostic value. The following gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) also showed that FKBP10 is mainly involved in cell adhesion process, while adhesion experiments confirmed that cell adhesion was down-regulated after silencing FKBP10 in GC cells, and adhesion-related molecules integrin αV and α 6 were down-regulated.
Conclusion: FKBP10 may be used as a marker for lymph node metastasis of GC and could be used as a potential target for future treatment of GC.
Keywords: FKBP10, GC, adhesion, lymph node metastasis, integrin