109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

甲基巴豆酰辅酶 A 羧化酶 2 通过调节 GLUT1-P38 MAPK 信号通路促进前列腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并抑制其细胞凋亡
Authors He J, Mao Y, Huang W, Li M, Zhang H, Qing Y, Lu S, Xiao H, Li K
Received 15 February 2020
Accepted for publication 8 July 2020
Published 28 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7317—7327
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S249906
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Purpose: Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common cancer in American men, and the mechanisms of development and progression are still not completely clear. Methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (MCCC2) was previously identified overexpressed in PCa with lymph node metastasis, but its specific role and mechanisms need further investigation. This study aimed to investigate the role of MCCC2 in PCa cells and its underlying mechanisms.
Materials and Methods: Quantitative RT-PCR and Western blotting were used to detect MCCC2 mRNA and protein expression in normal prostate epithelium and cancerous cells. Upon manipulation of MCCC2 expression, cell proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assays and migration and invasion were determined by transwell assays. Changes of apoptosis, cell cycle and mitochondrial membrane potential were evaluated by flow cytometry. MCCC2-mediated signaling pathways were screened by bioinformatics and verified by RT-PCR and Western blotting. Finally, immunohistochemistry was performed to detect the expression of MCCC2 and glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GLUD1) in PCa tissues to analyze their correlation.
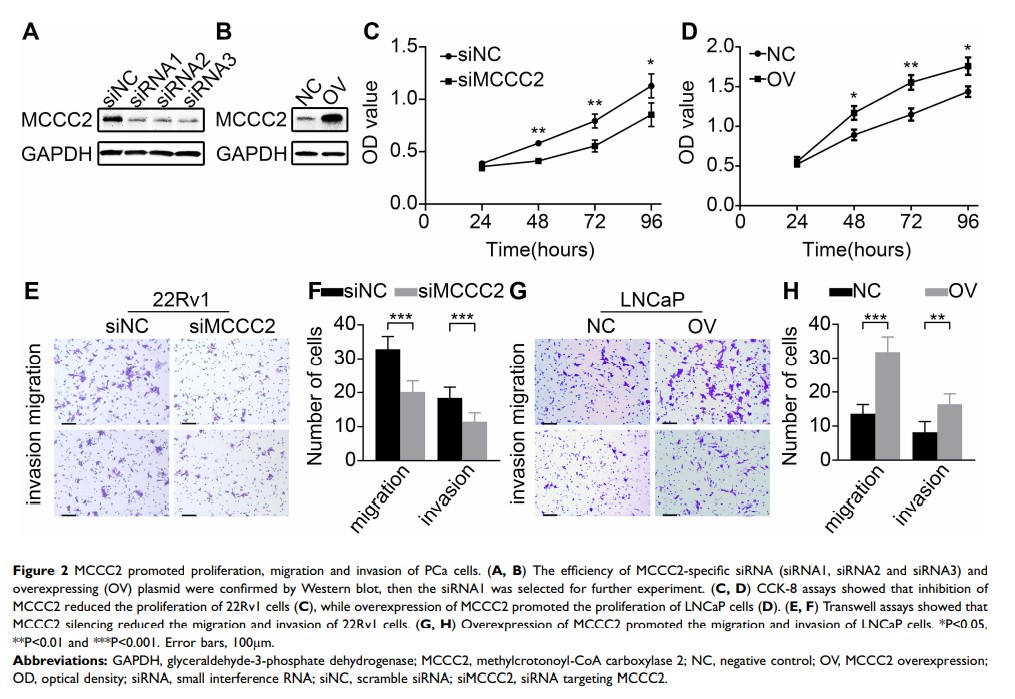
Results: We demonstrated that MCCC2 promoted cell proliferation, migration and invasion but inhibited apoptosis in PCa cells. In addition, MCCC2 in 22Rv1 cells induced mitochondrial damage. In PCa tissues, MCCC2 overexpression associated with lymph node metastasis (P =0.001) and high Gleason scores (P < 0.001). MCCC2 positively correlated with GLUD1 expression in PCa tissues (r=0.435, P < 0.001). Ectopic overexpression of MCCC2 up-regulated GLUD1 and p38 MAPK expression, whereas inhibition of MCCC2 decreased GLUD1 and p38 MAPK expression.
Conclusion: MCCC2 exerts oncogenic function in PCa through regulating GLUD1-p38 MAPK signaling pathway, and it may be a potential treatment target.
Keywords: prostate cancer, MCCC2, GLUD1, p38 MAPK