109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胰高血糖素样肽 1 可减轻脂毒性诱导的 ApoE–/– 小鼠胰岛功能障碍
Authors Liu F, Gong L, Qin W, Cui C, Chen L, Zhang M
Received 14 May 2020
Accepted for publication 8 July 2020
Published 28 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2701—2709
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S262479
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
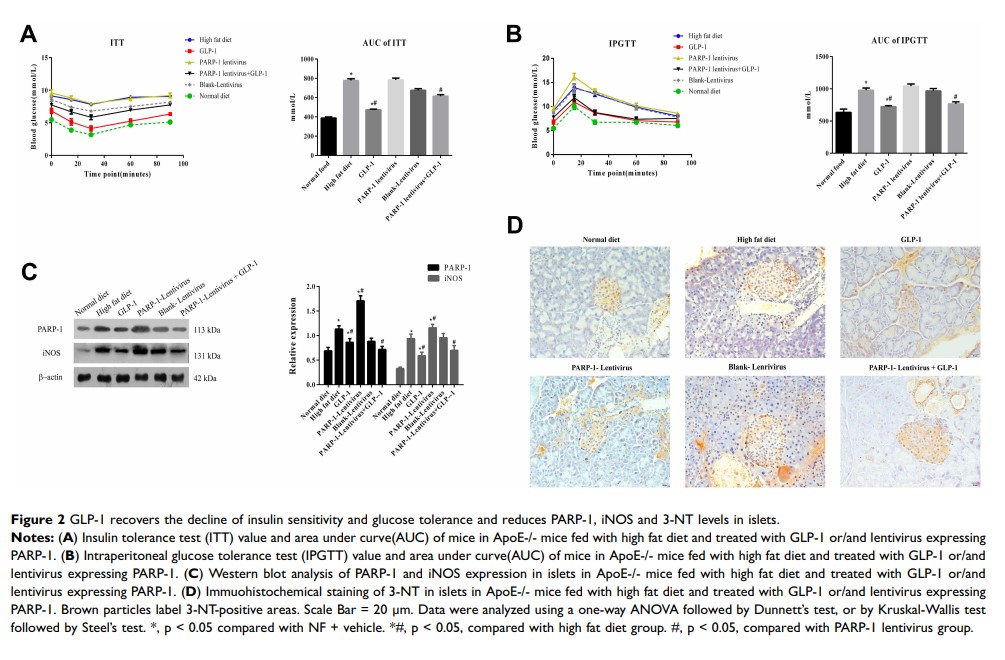
Aim: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1) is known to decrease glucagon release and may be beneficial for the reduction of elevated blood glucose. However, its role and mechanism of action in diabetes remain elusive. This study aimed to examine the function of GLP1 and analyze the mechanism of effect that GLP1exerts on inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in diabetic mice.
Methods: A diabetes model was established in ApoE–/– mice fed a high-fat diet and treated with GLP1 and/or lentivirus-expressing PARP1. PARP1, iNOS, and inflammatory factors in islets were detected by Western blot and ELISA. Islet α cells and β cells and CD8+ T lymphocytes were detected by immunostaining. Islet-cell apoptosis was detected by TUNEL.
Results: GLP1 inhibited the expression of PARP1 and iNOS in islets, alleviated decrease in β cells, and suppressed cell apoptosis induced by the high-fat diet. Moreover, GLP1 recovered the decline in insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in ApoE–/– mice fed the high-fat diet, and the effects of GLP1 were related to the inhibition of COX2 and NFκB expression.
Conclusion: GLP1 significantly alleviated the decrease in β-cell numbers, suppressed β-cell apoptosis induced by the high-fat diet, inhibited the expression of iNOS, and alleviated inflammatory islet injury via inhibiting the COX2–NFκB pathway.
Keywords: GLP1, islet function, PARP1