109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LINC01094 通过下调 miR-330-3p 及增强 MSI1 表达来促进神经胶质瘤的进展
Authors Zhu B, Liu W, Liu H, Xu Q, Xu W
Received 19 March 2020
Accepted for publication 23 June 2020
Published 28 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6511—6521
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254630
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: This study aims at probing into the expression, function, and mechanism of LINC01094 and miR-330-3p in glioma.
Materials and Methods: qRT-PCR was employed to examine LINC01094 and miR-330-3p expressions in gliomas. After gain-of-function and loss-of-function models were constructed, CCK-8 and Transwell assays were used to detect the proliferation, migration and invasion of LN229 and U251 cells, respectively. Additionally, dual luciferase reporter gene assay was utilized to verify the binding site between m4iR-330-3p and LINC01094, miR-330-3p, and the 3ʹUTR of musashi RNA binding protein 1 (MSI1). Then, RNA pull-down, RIP, qRT-PCR and Western blot were employed to detect the regulatory relationships among LINC01094, miR-330-3p, and MSI1.
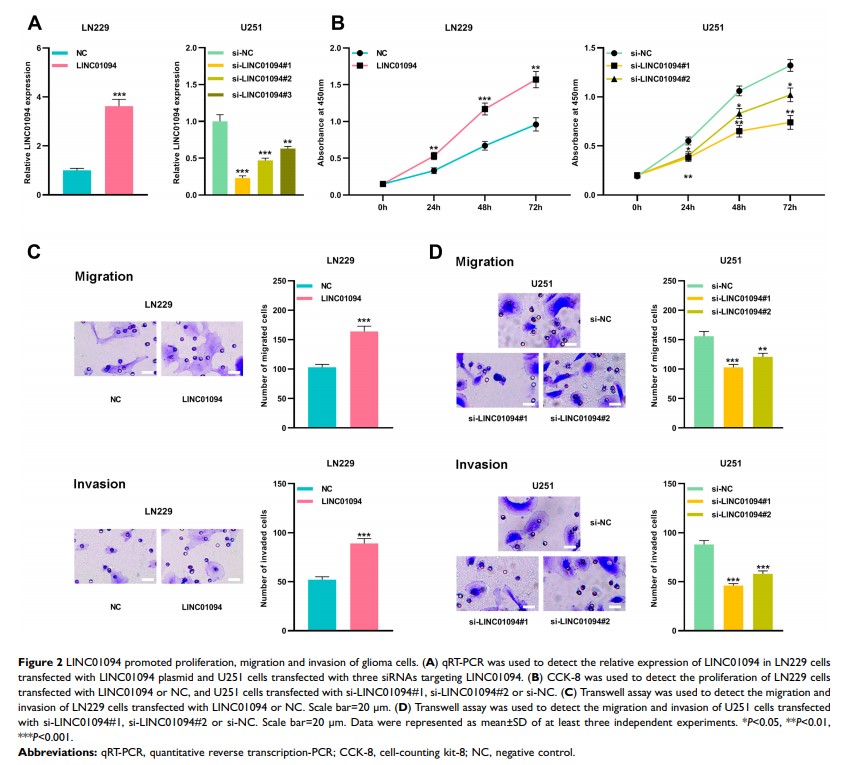
Results: The expression of LINC01094 was elevated in glioma tissues and cell lines, and the high expression of LINC01094 was associated with high grade of glioma. In contrast, miR-330-3p was lowly expressed in glioma tissue. Overexpression of LINC01094 or down-regulation of miR-330-3p promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells, while LINC01094 knockdown or miR-330-3p up-regulation impeded these processes. miR-330-3p was identified as a target miRNA of LINC01094, and it could be negatively regulated by LINC01094. In addition, miR-330-3p antagonized the function of LINC01094 by negatively regulating MSI1.
Conclusion: LINC01094 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells by adsorbing miR-330-3p and up-regulating the expression of MSI1.
Keywords: LINC01094, miR-330-3p, MSI1, glioma