109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二十碳五烯酸的 15-LOX-1 代谢可促进 miR-101 的表达,从而抑制结肠癌中的 Cox2 途径
Authors Cai Y, Liu J, Cai S, Miao E, Jia C, Fan Y, Li Y
Received 6 November 2019
Accepted for publication 6 April 2020
Published 15 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 5605—5616
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S237562
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Purpose: It is well known that diet Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is beneficial to colon cancer (CC). However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of EPA-relating miRNAs on genesis and development of this area is still unclear.
Materials and Methods: This study tries to find the function and specific role of EPA in CC through quantitative PCR (qPCR), Western blotting, immunofluorescence (IF), mass spectrometry, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays. By these methods, the enrichment of 15-LOX-1 metabolites of EPA, the expression of miR-101 and Cox2, and the relationship among them in CC are measured.
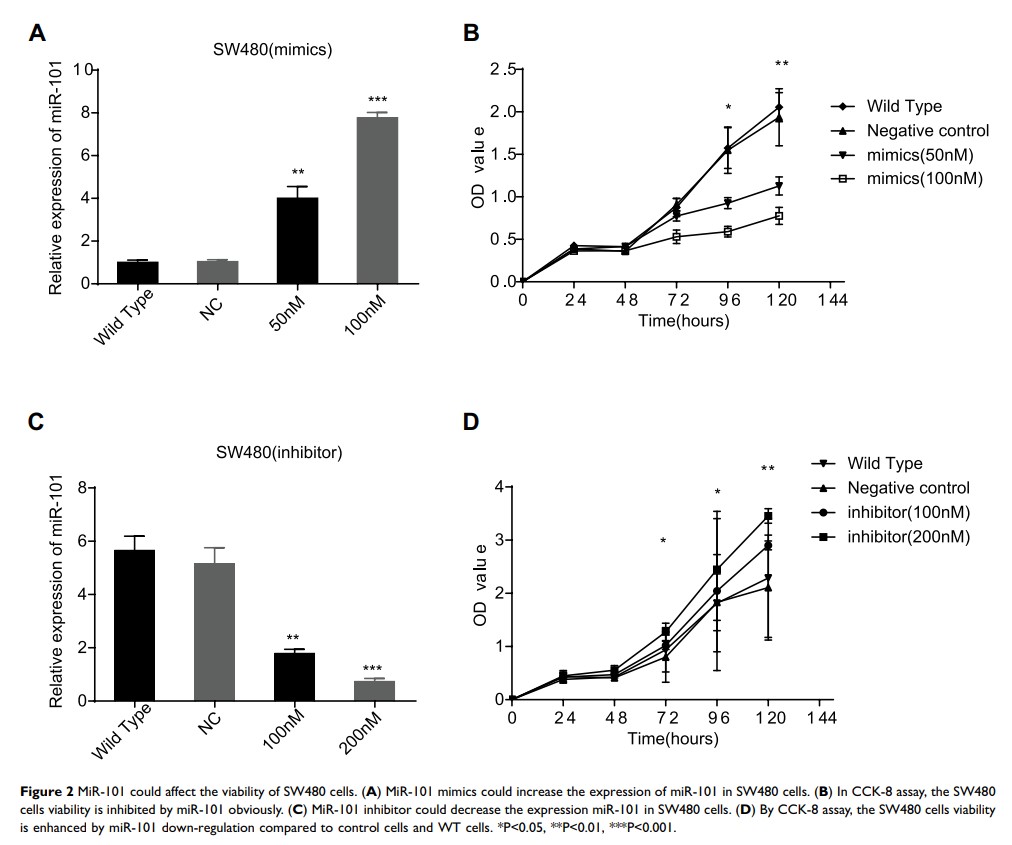
Results: The quantity of miR-101 was obviously suppressed in CC tissues and SW480 cells. After application of miR-101 mimics in CC cell lines, the Cox2 expression was inhibited too. Next, we confirmed that EPA could increase the expression of miR-101 induced by 15-LOX-1. Finally, we tested whether EPA functions as a regulator of miR-101 via the production of resolvin E3.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that the EPA– 15-LOX-1–miR-101-Cox2 signaling pathway owns a crucial position in the pathogenesis and development of diet-related CC. These findings exert exciting meanings for presenting new therapeutic angles in CC.
Keywords: colon cancer, 15-LOX-1, miR-101, Cox2, EPA