109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肺癌的联合化疗–使用由适体修饰的脂质体-聚合物杂化纳米粒子共同递送多西他赛(多烯紫杉醇)前体药物和顺铂
Authors Wu R, Zhang Z, Wang B, Chen G, Zhang Y, Deng H, Tang Z, Mao J, Wang L
Received 19 January 2020
Accepted for publication 15 April 2020
Published 9 June 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2249—2261
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S246574
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
Purpose: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Drug resistance is the major barrier for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The aim of this research is to develop an aptamer-decorated hybrid nanoparticle for the co-delivery of docetaxel prodrug (DTXp) and cisplatin (DDP) and to treat lung cancer.
Materials and Methods: Aptamer-conjugated lipid–polymer ligands and redox-sensitive docetaxel prodrug were synthesized. DTXp and DDP were loaded into the lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPHNs). The targeted efficiency of aptamer-decorated, DTXp and DDP co-encapsulated LPHNs (APT-DTXp/DDP-LPHNs) was determined by performing a cell uptake assay by flow cytometry-based analysis. In vivo biodistribution and anticancer efficiency of APT-DTXp/DDP-LPHNs were evaluated on NSCLC-bearing mice xenograft.
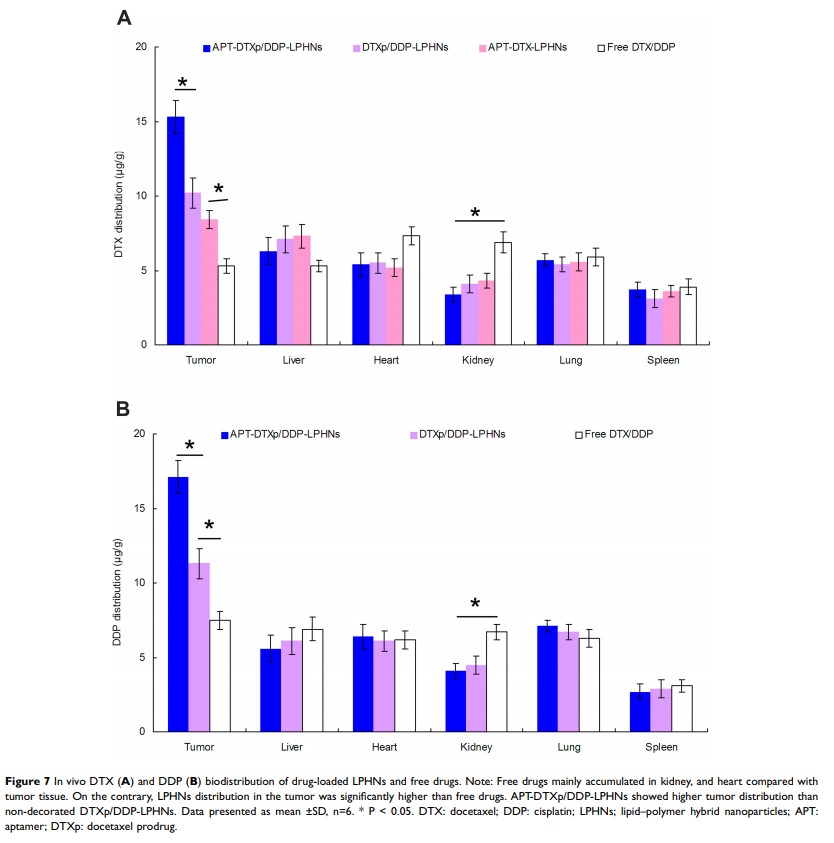
Results: APT-DTXp/DDP-LPHNs had a particle size of 213.5 ± 5.3 nm, with a zeta potential of 15.9 ± 1.9 mV. APT-DTXp/DDP-LPHNs exhibited a significantly enhanced cytotoxicity (drug concentration causing 50% inhibition was 0.71 ± 0.09 μg/mL), synergy antitumor effect (combination index was 0.62), and profound tumor inhibition ability (tumor inhibition ratio of 81.4%) compared with the non-aptamer-decorated LPHNs and single drug-loaded LPHNs.
Conclusion: Since the synergistic effect of the drugs was found in this system, it would have great potential to inhibit lung tumor cells and in vivo tumor growth.
Keywords: lung cancer, combination therapy, docetaxel prodrug, cisplatin, aptamer-decorated, lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles