109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低温血浆通过调节 miR-203a/BIRC5 轴抑制肺癌细胞的增殖并诱导其细胞凋亡
Authors Yang Y, Li D, Li Y, Jiang Q, Sun R, Liu J, Wu F, Miao J, Ni L, Shi X, Huang C
Received 5 January 2020
Accepted for publication 9 April 2020
Published 8 June 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 5145—5153
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S244853
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
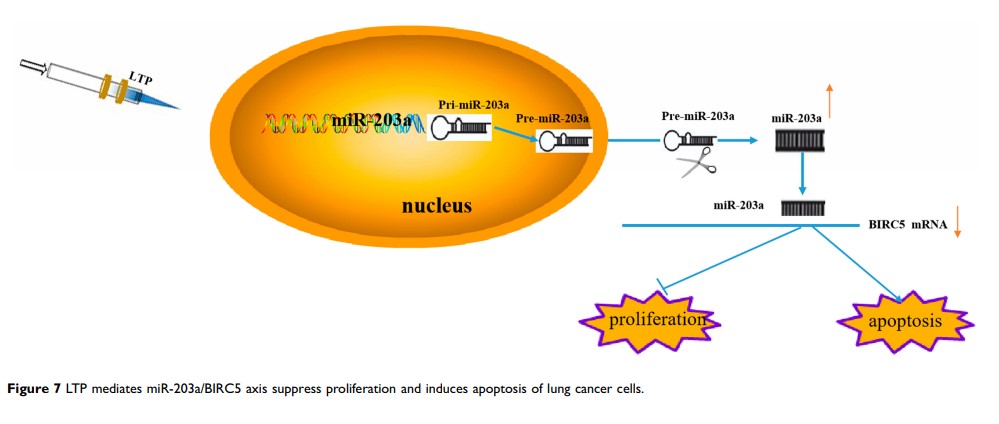
Aim: Low-temperature plasma (LTP) has potential applications in cancer therapy. Herein, we explored the molecular mechanisms of proliferation inhibition induced by LTP.
Methods: LTP was generated by a helium atmospheric-pressure plasma jet and used to treat A549 and H1299 cells. CCK-8 and cell apoptosis assays were performed to evaluate the effects of LTP treatment on A549 and H1299 cells. The qRT-PCR was performed to measure the expression of miR-203a after treating with LTP. CCK-8, colony formation, cell apoptosis assays, and Western blotting were performed to analyse the function of miR-203a in the development of lung cancer. Dual-luciferase assay and Western blotting were used to probe the relationship between miR-203a and BIRC5, and gene silencing using si-BIRC5 was carried out to explore the effect of knocking down BIRC5 on lung cancer cells.
Results: We found that LTP significantly suppressed proliferation and promoted apoptosis in A549 and H1299 cells. The miR-203a expression was increased after cells were treated with LTP. The miR-203a expression was downregulated among lung cancer tissue samples, and overexpression of miR-203a suppressed cell growth and induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells. We showed that miR-203a targeted BIRC5. Moreover, silencing of BIRC5 caused proliferation inhibition and induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our study revealed that LTP inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in A549 and H1299 cells through the miR-203a/BIRC5 axis. These findings showed that LTP could potentially be used to treat lung cancer.
Keywords: low-temperature plasma, lung cancer, proliferation, miR-203a, BIRC5