109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
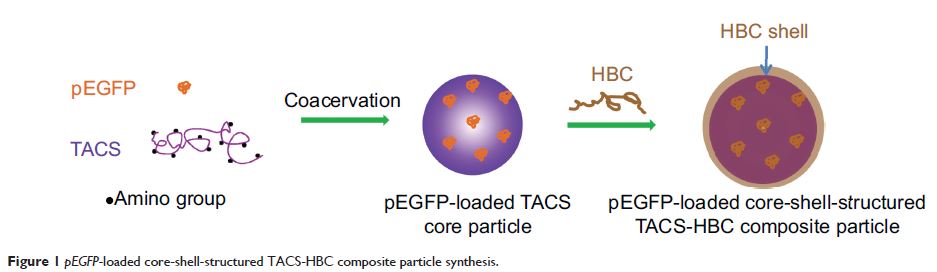
pEGFP - 装载芯-壳结构的脱乙酰壳多糖复合颗粒缓释行为及其在体内、体外的转染
Authors Wang Y, Lin FX, Zhao Y, Wang MZ, Ge XW, Gong ZX, Bao DD, Gu YF
Published Date October 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 4965—4978
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S58104
Received 22 November 2013, Accepted 3 April 2014, Published 23 October 2014
Abstract: Novel submicron core-shell-structured chitosan-based composite particles encapsulated with enhanced green fluorescent protein plasmids (pEGFP ) were prepared by complex coacervation method. The core was pEGFP -loaded thiolated N-alkylated chitosan (TACS) and the shell was pH- and temperature-responsive hydroxybutyl chitosan (HBC). pEGFP -loaded TACS-HBC composite particles were spherical, and had a mean diameter of approximately 120 nm, as measured by transmission electron microscopy and particle size analyzer. pEGFP showed sustained release in vitro for >15 days. Furthermore, in vitro transfection in human embryonic kidney 293T and human cervix epithelial cells, and in vivo transfection in mice skeletal muscle of loaded pEGFP , were investigated. Results showed that the expression of loaded pEGFP , both in vitro and in vivo, was slow but could be sustained over a long period. pEGFP expression in mice skeletal muscle was sustained for >60 days. This work indicates that these submicron core-shell-structured chitosan-based composite particles could potentially be used as a gene vector for in vivo controlled gene transfection.
Keywords: gene therapy, gene transfection, hydroxybutyl chitosan, thiolated N-alkylated chitosan, pEGFP , complex coacervation
Keywords: gene therapy, gene transfection, hydroxybutyl chitosan, thiolated N-alkylated chitosan, pEGFP , complex coacervation