109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
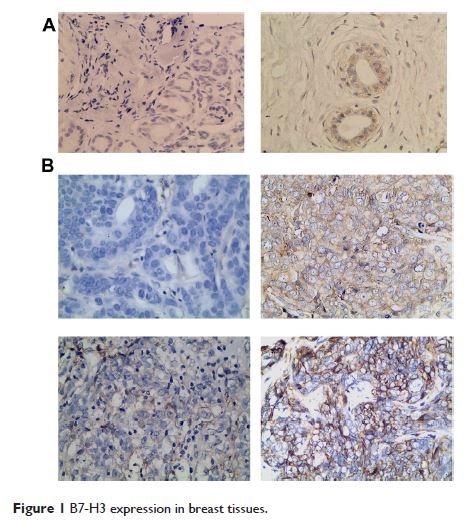
在乳腺癌中 B7-H3 的表达与通过基因沉默上调 VEGF
Authors Sun J, Guo YD, Li XN, Zhang YQ, Gu L, Wu PP, Bai GH, Xiao Y
Published Date October 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1979—1986
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S63424
Received 3 March 2014, Accepted 26 June 2014, Published 29 October 2014
Abstract: B7-H3, a novel member of the B7 family, was previously known as a regulatory ligand regulating T-cell-mediated immune response, and in recent years it was found to take a significant role in various cancers. In some tumor types, high expression of B7-H3 had been linked to a poor prognosis, whereas in other cancers the opposite effect had been observed. The precise role of B7-H3 in tumor immunity is unclear, and further investigations are needed. In the present study, we studied the expression of B7-H3 in the pathologic specimens of 221 patients treated for breast cancer by immunohistochemistry. Strong B7-H3 expression was found in cancer tissues from 80.55% patients, and B7-H3 expression had a negative relation with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, microvascular density for CD34, and tumor size. Furthermore, through lipopolysaccharide-mediated delivery of stable short hairpin ribonucleic acid we observed that silencing of B7-H3 could increase the transcription and secreting of VEGF in breast cancer cell line MCF-7. In summary, the present study demonstrated that B7-H3 suppressed tumor growth through inhibiting VEGF expression. These results increased knowledge of the nonimmunological role of B7-H3 protein and provided novel insights into great biological functions and a putative therapeutic target in breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, B7-H3, vascular endothelial growth factor
Keywords: breast cancer, B7-H3, vascular endothelial growth factor