109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

网络药理学方法和薄层色谱分析方法相结合对伸筋活血合剂的关键活性成分及其在骨关节炎治疗中的消炎和镇痛作用进行验证
Authors Yu MX, Ma XQ, Song X, Huang YM, Jiang HT, Wang J, Yang WH
Received 27 December 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2020
Published 16 March 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1145—1156
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S243951
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
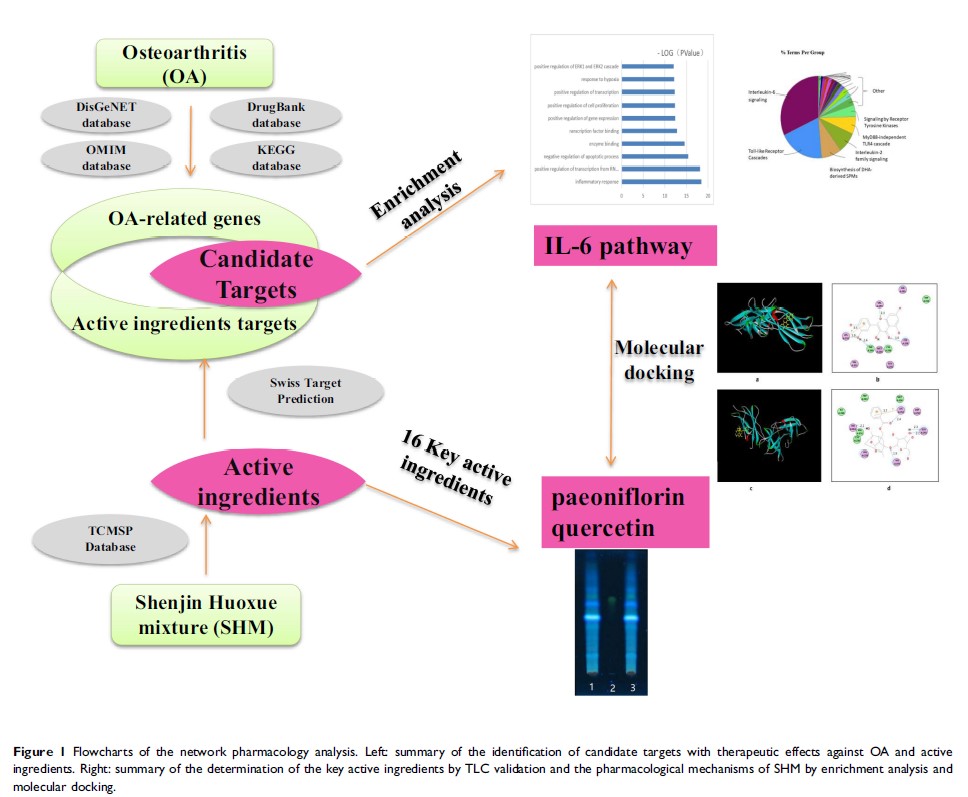
Background: Shenjin Huoxue Mixture (SHM), a classic traditional herb mixture has shown significant clinical efficacy against osteoarthritis (OA). Our previous experimental study has confirmed its anti–inflammatory and analgesic effect on acute soft tissue injury in rats, with the compound of glycyrrhizinate in SHM identified and the content of paeoniflorin in SHM determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). However, the components and its pharmacological mechanisms of SHM against OA have not been systematically elucidated yet. Thus this study aimed to predict the key active ingredients and potential pharmacological mechanisms of SHM in the treatment of OA by network pharmacology approach and thin-layer chromatography (TLC) validation.
Methods: The active ingredients of SHM and their targets, as well as OA-related targets, were identified from databases. The key active ingredients were defined and ranked by the number of articles retrieved in PubMed using the keyword “(the active ingredients [Title/Abstract]) AND Osteoarthritis[Title/Abstract] ”, and validated partially by TLC. The pharmacological mechanisms of SHM against OA were displayed by GO term and Reactome pathway enrichment analysis with Discovery Studio 3.0 software docking to testing the reliability.
Results: Finally, 16 key active ingredients were identified and ranked, including quercetin validated through TLC. Inflammatory response, IL-6 signaling pathway and toll-like receptor (TLR) cascades pathway were predicted as the main pharmacological mechanisms of SHM against OA. Especially, 12 out of 16 key active ingredients, including validated quercetin, were well docked to IL-6 proteins.
Conclusion: Our results confirmed the anti–inflammatory and analgesic effect of SHM against OA through multiple components, multiple targets and multiple pathways, which revealed the theoretical basis of SHM against OA and may provide a new drug option for treating OA.
Keywords: Shenjin Huoxue Mixture, osteoarthritis, active ingredients, pharmacological mechanisms, network pharmacology, thin-layer chromatography