109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

新颖的乳铁蛋白结合的两亲性聚合物 (氨基乙基乙烯酯)/聚 (L-丙交酯) 的共聚物纳米气泡用于肿瘤靶向超声成像
Authors Luo BH, Liang HG, Zhang SW, Qin XJ, Liu XH, Liu W, Zeng FQ, Wu Y, Yang XL
Received 27 February 2015
Accepted for publication 30 April 2015
Published 16 September 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5805—5817
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S83582
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
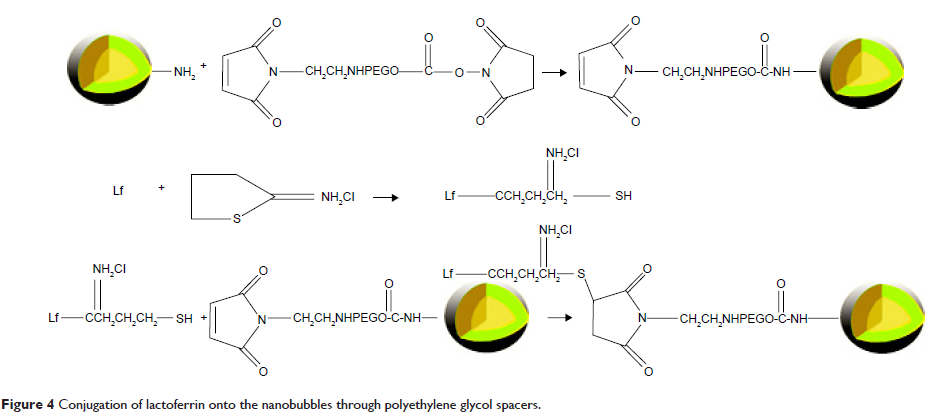
Abstract: In the study reported here, a novel amphiphilic poly(aminoethyl ethylene phosphate)/poly(L-lactide) (PAEEP-PLLA) copolymer was synthesized by ring-opening polymerization reaction. The perfluoropentane-filled PAEEP-PLLA nanobubbles (NBs) were prepared using the O1/O2/W double-emulsion and solvent-evaporation method, with the copolymer as the shell and liquid perfluoropentane as the core of NBs. The prepared NBs were further conjugated with lactoferrin (Lf) for tumor-cell targeting. The resulting Lf-conjugated amphiphilic poly(aminoethyl ethylene phosphate)/poly(L-lactide) nanobubbles (Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs) were characterized by photon correlation spectroscopy, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The average size of the Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs was 328.4±5.1 nm, with polydispersity index of 0.167±0.020, and zeta potential of -12.6±0.3 mV. Transmission electron microscopy imaging showed that the Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs had a near-spherical structure, were quite monodisperse, and there was a clear interface between the copolymer shell and the liquid core inside the NBs. The Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs also exhibited good biocompatibility in cytotoxicity and hemolysis studies and good stability during storage. The high cellular uptake of Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs in C6 cells (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1-positive cells) at concentrations of 0–20 µg/mL indicated that the Lf provided effective targeting for brain-tumor cells. The in vitro acoustic behavior of Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs was evaluated using a B-mode clinical ultrasound imaging system. In vivo ultrasound imaging was performed on tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice, and compared with SonoVue® microbubbles, a commercial ultrasonic contrast agent. Both in vitro and in vivo ultrasound imaging indicated that the Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs possessed strong, long-lasting, and tumor-enhanced ultrasonic contrast ability. Taken together, these results indicate that Lf-PAEEP-PLLA NBs represent a promising nano-sized ultrasonic contrast agent for tumor-targeting ultrasonic imaging.
Keywords: PAEEP-PLLA copolymer,in vitro acoustic behavior, in vivo ultrasonic imaging, SonoVue ® microbubbles